HTRF Total IR-β (Insulin Receptor β) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points
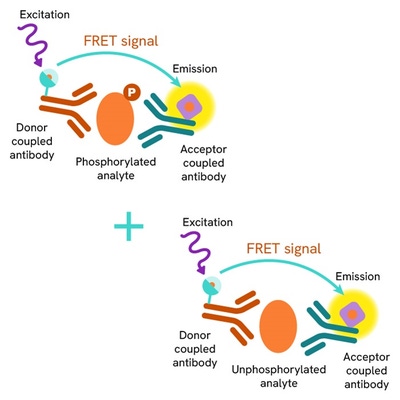

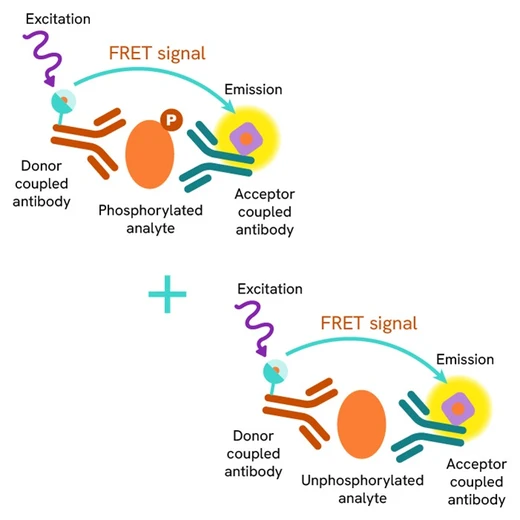




This HTRF assay enables the detection of cellular Insulin Receptor beta and can be used as a normalization assay for the phospho-IR beta kit.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Cell Signaling |
| Sample Volume | 16 µL |
This HTRF assay enables the detection of cellular Insulin Receptor beta and can be used as a normalization assay for the phospho-IR beta kit.









Product information
Overview
Total Insulin Receptor-ß assay enables the detection of Total Insulin Receptor-ß. Stimulated by insulin and insulin-like growth factors, the insulin receptor is involved in several pathways such as those for Insulin and FoxO signaling.
HTRF assays offer many advantages over other technologies:
- Homogeneous add-and-read format
- No wash steps
- Low background
- Straightforward miniaturization from 96- or 384-well microplates to high density assay formats such as 384-well low volume and 1536-well plates
- Stable signal, providing flexibility in time of readout or size of assays
How it works
Total-Insulin Receptor ß assay principle
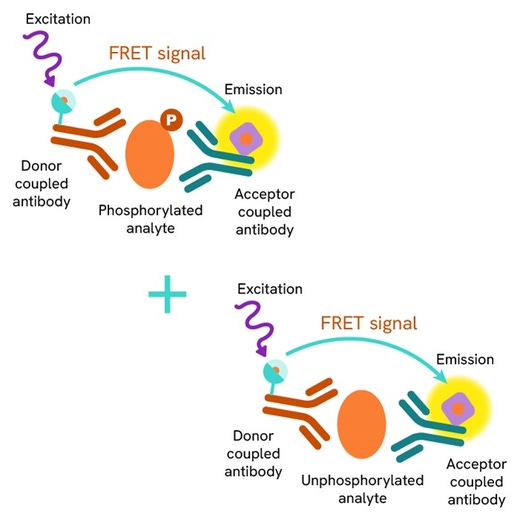
The Total-Insulin Receptor ß assay quantifies the expression level of Insulin Receptor ß in a cell lysate. Contrary to Western Blot, the assay is entirely plate-based and does not require gels, electrophoresis or transfer. The Total-Insulin Receptor ß assay uses two labeled antibodies: one coupled to a donor fluorophore, the other to an acceptor. Both antibodies are highly specific for a distinct epitope on the protein. In presence of Insulin Receptor ß in a cell extract, the addition of these conjugates brings the donor fluorophore into close proximity with the acceptor and thereby generates a FRET signal. Its intensity is directly proportional to the concentration of the protein present in the sample, and provides a means of assessing the proteins expression under a no-wash assay format.

Total-Insulin Receptor ß 2-plate assay protocol
The 2 plate protocol involves culturing cells in a 96-well plate before lysis then transferring lysates to a 384-well low volume detection plate before adding Total Insulin Receptor ß HTRF detection reagents. This protocol enables the cells' viability and confluence to be monitored

Total-insulin receptor ß 1-plate assay protocol
Detection of total Insulin Receptor ß with HTRF reagents can be performed in a single plate used for culturing, stimulation and lysis. No washing steps are required. This HTS designed protocol enables miniaturization while maintaining robust HTRF quality.

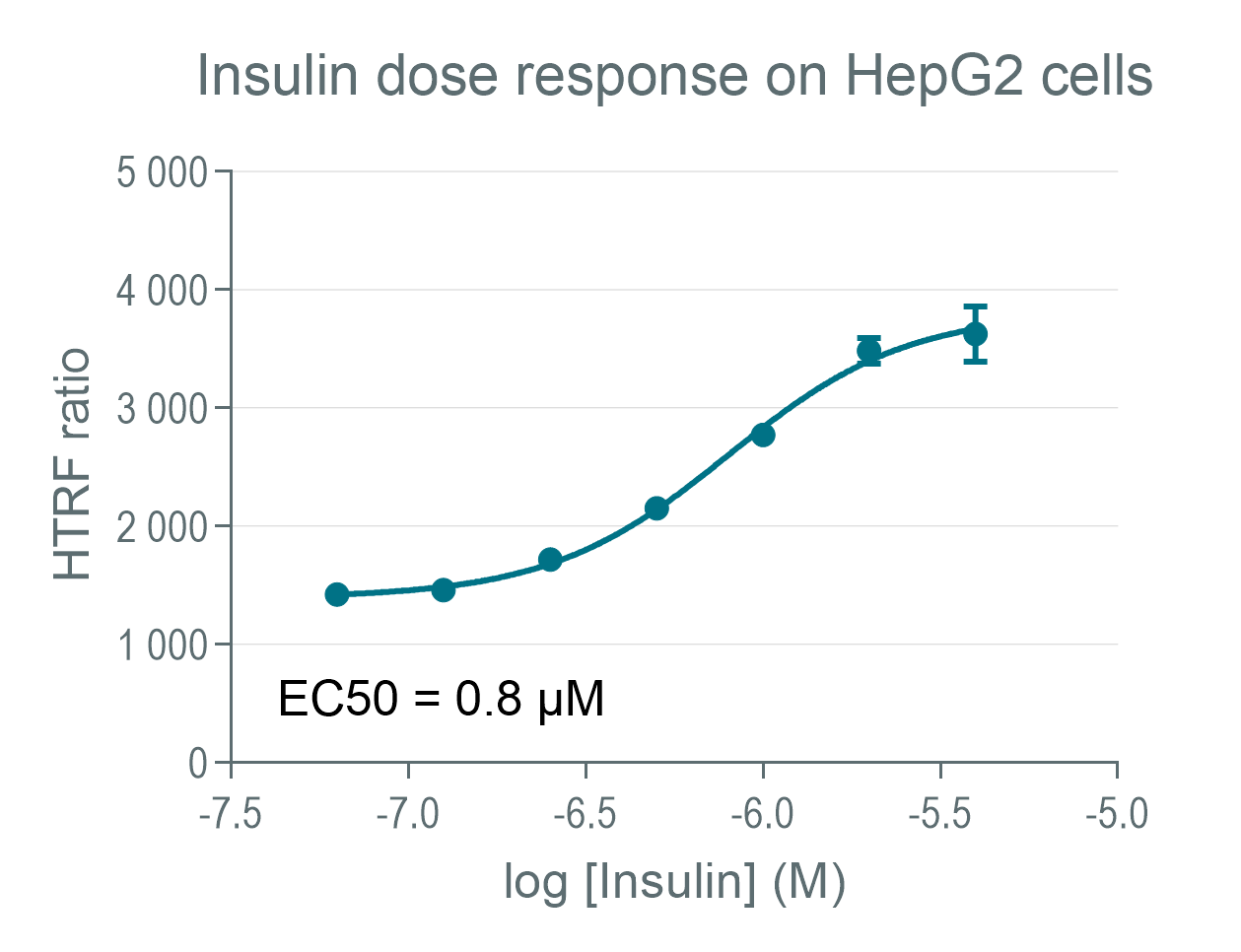
Total-IRβ (Tyr1150/1151) illustration on HepaRG
HepaRG cells were plated at 200,000 cells per well on a 96-well plate. After an incubation of 5 days at 37°C, 5% CO2, a serial dilution of insulin was added under cells in presence of pervanadate at 30µM for 5 minutes at 37°C, 5% CO2. Stimulation medium was removed from cells and 50µL of lysis buffer was added onto the cells. Lysis step was done by shaking gently during 30 minutes. 16µL of samples were transferred in a 384-well small volume plate then 4µL of phospho IRβ HTRF detection reagents were added. In parrallel 16µl were dispensed on other wells than 4µL of total IRβ HTRF detection reagents were added. Signals were recored overnight.
Total-IRβ WB comparison
Human Hek 293 cells were cultured to 80% confluency. After insulin and pervanadate co-treatment, cells were lysed and soluble supernatants were collected via centrifugation. Serial dilutions of the cell lysate were performed and 16 µL of each dilution were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate before finally adding phospho IRβ HTRF cellular kit reagents. A side by side comparison showed the HTRF Phospho assay is at least 8-fold more sensitive than the Western Blot.

Specifications
| Application |
Cell Signaling
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Molecular Modification |
Total
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
16 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target Class |
Phosphoproteins
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Metabolism/Diabetes
Neuroscience
|
| Unit Size |
500 assay points
|
Video gallery
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
This guide provides you an overview of HTRF applications in several therapeutic areas.
This flyer details HTRF™ and AlphaLISA™ assays for investigating key biomarkers and signaling pathways in metabolic disease...
Obesity is a complex condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation, posing significant health and socioeconomic challenges...


Loading...
How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.