HTRF Human H232 STING Binding Kit, 500 Assay Points





This HTRF assay is designed to select and characterize compounds that specifically bind human H232 STING protein.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Protein-Protein Interaction |
| Sample Volume | 5 µL |
This HTRF assay is designed to select and characterize compounds that specifically bind human H232 STING protein.









Product information
Overview
A fast and easy way to identify new binders to human H232 STING.
Stimulator of interferon genes (STING), also known as transmembrane protein 173 (TMEM173), is a protein playing a major role in innate immunity.
The H232 variant is found in 13.7% of the world population. Upon intracellular cytosolic DNA release from pathogens such as viruses and bacteria, 2’-3’cGAMP binds to STING protein and triggers the secretion of type 1 interferon. However, the H232 variant is known to poorly bind 2'-3'cGAMP and other natural dinucleotides. The quest for molecules that are effective against all genetic variants has become crucial to modulate immunity in autoinflammatory diseases.
HTRF assays offer many advantages over other technologies:
- Homogeneous add-and-read format
- No wash steps
- Low background
- Straightforward miniaturization from 96- or 384-well microplates to high density assay formats such as 384-well low volume and 1536-well plates
- Stable signal, providing flexibility in time of readout or size of assays
How it works
Assy principle
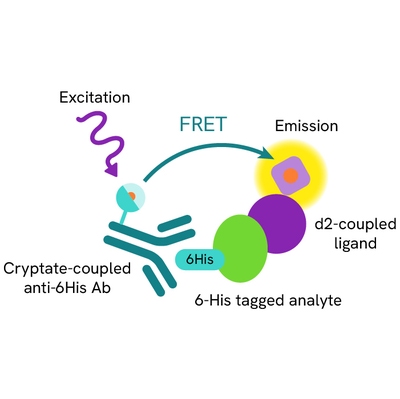
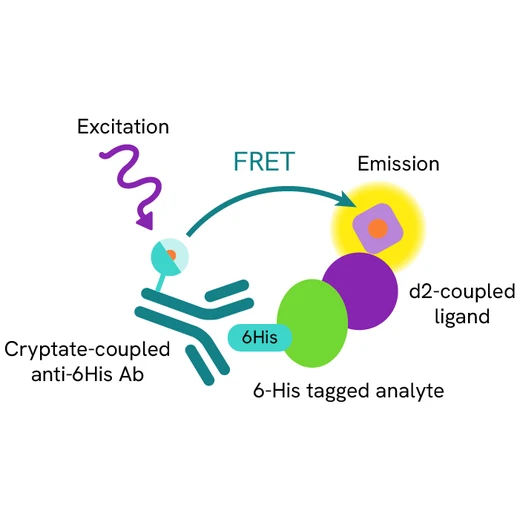
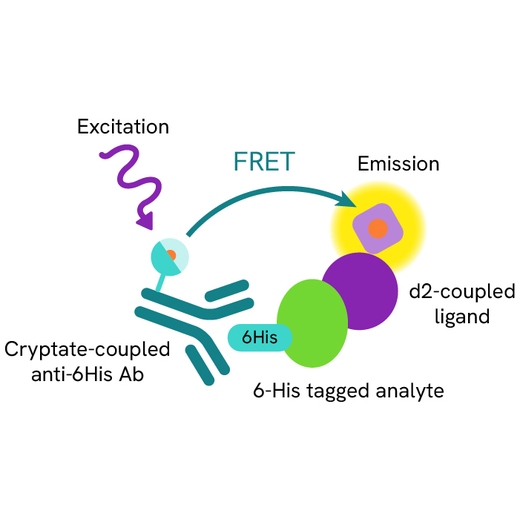
The HTRF H232 STING binding assay is a competitive assay format which uses d2-labeled H232 STING ligand, a 6His tagged human H232 STING protein, and an anti 6His Cryptate-labeled antibody. Your compound competes with the H232 STING ligand-d2 and thereby prevents FRET from occurring.

Assay protocol
The Human H232 STING binding assay can be run in a 96- or 384-well low volume white plate (20 µL final). As described here, samples or standards are dispensed directly into the assay plate. The human His-tagged H232 STING protein is then added, followed by the dispensing of the HTRF reagents: the anti 6His antibody labeled with Terbium cryptate and the H232 STING ligand labeled with d2. The reagents labeled with HTRF fluorophores may be pre-mixed and added in a single dispensing step. No washing steps are needed. The protocol can be further miniaturized or upscaled by simply resizing each addition volume proportionally.

Assay validation
Compound screening
Various compounds known to be STING ligands were added to the assay.
2'3'cGAMP displays a low affinity for the H232 variant in the µM range, compared its high affinity against WT Sting (Ki=2.5nM). Similarly, the other bacterial compounds such as 3'3' cGAMP, cyclic di-AMP, and cyclic d-GMP, or the reference compound ADU-S100, show Ki constants in the µM.
The assay standard corresponding to a derivative of the labeled ligand is more potent, with a Ki at 13.4nM.
DMXAA, a non-specific compound and also a well-known mouse STING binder, has no effect on the assay, confirming the human specificity of the kit.

Simplified pathway
STING simplified pathway
STING, for STimulator of INterferon Genes, is a cytoplasmic homodimeric protein localized in the endoplasmic reticulum and which plays an essential role in innate immunity. Upon pathogen infection or mitochrondrial shrinking during apoptosis, floating dsDNAs bind and activate a DNA sensor, cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS). Activated cGAS leads to the production of 2’-3’cGAMP, a cyclic dinucleotide, which then binds to STING proteins. In turn, phosphorylated STING interacts with TANK-binding-kinase-I (TBK1), leading to the recruitment and activation of the active interferon regulatory factor (IRF3) dimer. Nuclear translocation of the IRF3 dimer leads to the transcription of genes encoding IFN-α/β. In addition, the STING pathway controls NF-κB dependent inflammatory cytokine expression. As a negative feedback loop, the DNA-stimulated cGAS-STING-TBK1 pathway also triggers STING protein degradation through p62 SQSTM1 associated autophagy, to switch off IFNb production.

Specifications
| Application |
Protein-Protein Interaction
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Cellular or Signaling Pathway |
Inflammasome/Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
5 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target Class |
Binding Assay
|
| Target Species |
Human
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Infectious Diseases
Oncology & Inflammation
|
| Unit Size |
500 assay points
|
Video gallery
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
This guide provides you an overview of HTRF applications in several therapeutic areas.


Loading...
How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.