HTRF Human and Mouse HIF-1α Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points
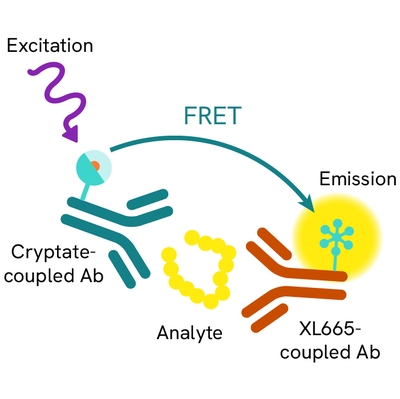

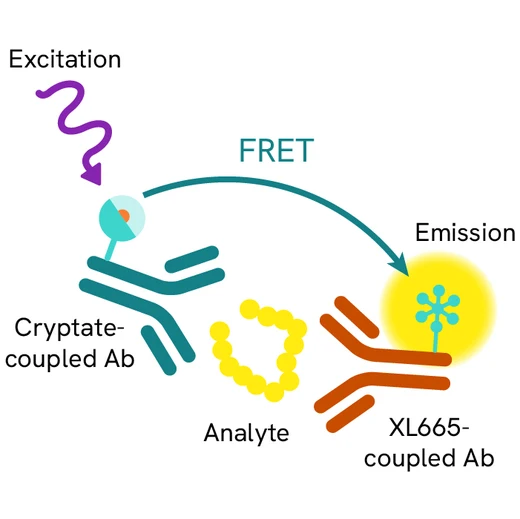




The HIF-1a assay is intended to measure this master transcriptional regulator of cellular and developmental response to hypoxia.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Protein Quantification |
| Sample Volume | 16 µL |
The HIF-1a assay is intended to measure this master transcriptional regulator of cellular and developmental response to hypoxia.









Product information
Overview
HIF-1a is one of the 2 subunits of the transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). HIF-1 acts as a master regulator of cellular and systemic response to hypoxia by activating the translation of genes involved in energy metabolism, angiogenesis, and apoptosis, among others. High levels of HIF-1 have been associated with aggressive tumor progression. HIF-1a is also strongly linked to diabetes through its involvement in the glucose uptake of target cells. It has also been implicated in diabetes complications, such as diabetic nephropathy or diabetic wound repair.
How it works
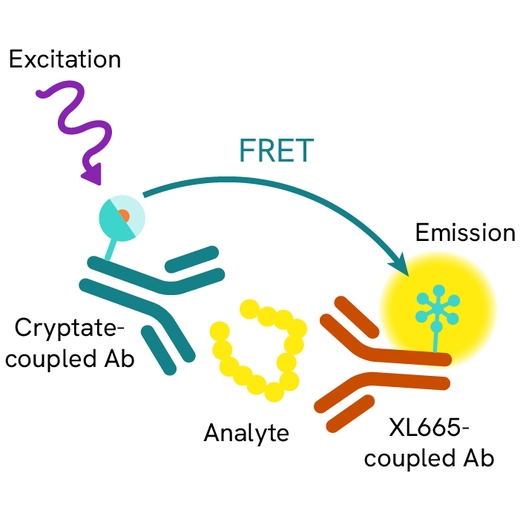
Assay principle
The HIF-1a HTRF assay is a sandwich immunoassay involving two specific anti-human anti-HIF-1a antibodies, respectively labelled with Europium Cryptate (donor) and d2 (acceptor). The intensity of the signal is proportional to the concentration of anti-HIF-1a present in the sample. The detection reagents may be pre-mixed and added in a single dispensing step for direct detection. No washing is needed at any step. After cell lysis, HIF-1a can be detected using the HTRF HIF-1a cellular assay kit reagents and most TR-FRET multimode plate readers.

Assay Protocol
Two-plate assay protocol Cells are plated, stimulated, and lysed in the same 96-well culture plate. Lysates are then transferred to the assay plate for the detection of HIF-1a by HTRF reagents. This protocol enables the cells' viability and confluence to be monitored. The antibodies labelled with HTRF fluorophores may be pre-mixed and added in a single dispensing step to further streamline the assay procedure. The assay detection can be run in 96- to 384-well plates by simply resizing each addition volume proportionally.

Assay validation
HTRF assay compared to Western Blot
Human HeLa cervical cancer cells were seeded in a T175 flask in complete culture medium, and incubated for 2 days at 37°C, 5% CO2 until 80% confluence was reached. After treatment (6 hours, 10 µM MG-132, 1 mM DMOG), the cells were lysed with 3 mL of supplemented lysis buffer#4 for 30 min at RT under gentle shaking. Soluble supernatants were collected after a 10 minute centrifugation. Serial dilutions of the cell lysate were performed in the supplemented lysis buffer and 16 µL of each dilution were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate before the addition of 4 µL of the HTRF HIF-1a detection reagents. Equal amounts of lysates were used for a side-by-side comparison of Western Blot and HTRF®. Using HTRF®, just 3120 cells were sufficient for minimal signal detection while 25,000 cells were needed for a Western Blot signal. The HTRF® assay is 8-fold more sensitive than the Western Blot.

Hydroxylase and Proteasome inhibitors effect
Murine embryonic fibroblasts NIH-3T37 were plated at 100,000 cells/well in a 96 well plate. After treatment for 6 hours at 37°C (in triplicate) with increasing concentrations of the hydroxylase inhibitor DMOG to prevent HIF-1a hydroxylation, or with increasing concentrations of the proteasome inhibitor MG-132 to inhibit HIF-1a degradation, the medium was removed and the cells were lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer #4 for 30 min at RT under gentle shaking. 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well for the HTRF detection.


HIF-1a and Phospho-Erk1/2 correlation
Human A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells were plated at 100,000 cells/well in a 96 well plate. After a preincubation with 1mM DFO for 30 minutes to prevent the degradation of HIF-1a, the cells were treated for 6 h at 37°C with increasing concentrations of EGF to activate the ERK pathway and the translation of HIF-1a. The medium was then removed and the cells were lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer#4 for 30min at RT under gentle shaking. 16 µL of lysate were then transferred into 2 different wells of a 384-sv plate for measurement in parallel.

HIF-1A upregulation upon IGF-1 stimulation
Human MCF-7 epidermoid carcinoma cells were plated at 50,000 cells/well in a 96 well plate. After a preincubation with 1mM DFO for 30 minutes to prevent the degradation of HIF-1a, the cells were treated for 6 h at 37°C with increasing concentrations of IG-1F to activate the AKT pathway and the translation of HIF-1a. The medium was then removed and the cells were lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer#4 for 30 min at RT under gentle shaking. 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate for detection.

HIF-1A and Phospho-AKT downregulation upon PI3K inhibitor treatment
Human MCF-7 epidermoid carcinoma cells were plated at 50,000 cells/well in a 96 well plate. After a preincubation with increasing concentrations of 1mM DFO for 30 minutes to prevent the degradation of HIF-1α , the cells were treated for 6 h at 37°C with increasing concentrations of the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 for 30 minutes (in triplicate) to inhibit the PI3K/AKT pathway. The cells were then activated with 10 nM IGF-1 and 1mM DFO. Next, the medium was removed and the cells were lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer#4 for 30 min at RT under gentle shaking. 16 µL of lysate were then transferred into 2 different wells of a 384-sv plate for measurement in parallel.

Simplified pathway
HIF1 consists of a constitutively expressed HIF-1ß subunit (87 kDa) and an O2-regulated HIF-1a subunit (120 kDa) which contains an O2-dependent degradation domain (ODD). Under normoxia, HIF-1a is hydroxylated on its ODD domain by O2-activated prolyl hydroxylases (PHDs), leading to its rapid ubiquitination and subsequent degradation by the proteasome.
Under hypoxia, PHD activity is inhibited and HIF-1a accumulates in the cytosol, translocates to the nucleus, heterodimerizes with HIF-1ß, and is activated. The complex activates the transcription of more than 100 target genes that facilitate responses to the hypoxic environment by encoding proteins involved in angiogenesis, erythropoiesis, cell proliferation/survival, and inflammation.

Specifications
| Application |
Protein Quantification
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
16 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target Class |
Biomarkers
|
| Target Species |
Human
Mouse
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Metabolism/Diabetes
NASH/Fibrosis
Oncology & Inflammation
|
| Unit Size |
500 assay points
|
Video gallery
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
Discover the versatility and precision of Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF) technology. Our HTRF portfolio offers a...
This guide provides you an overview of HTRF applications in several therapeutic areas.
An in-depth review of molecular and cellular pathways
The maintenance of proteostasis, the biological mechanisms that control the...


Loading...
How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.