HTRF Human and Mouse PARP cleaved-Asp214 Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points





| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Protein Quantification |
| Sample Volume | 16 µL |









Product information
Overview
The cleaved PARP (Asp214) kit enables the specific and quantitative detection of endogenous levels of the human, mouse, and monkey large fragment (89-kDa) of PARP-1. With its central position downstream from caspases 3 and 7, both activated by extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis pathways, cleaved PARP-1 represents a pertinent marker of cells undergoing apoptosis. Deregulated apoptosis plays a role in various diseases involving insufficient cell death, such as cancer, autoimmunity, and persistent infections, whereas excessive apoptosis can contribute to neuro-degeneration and ischaemia.
How it works
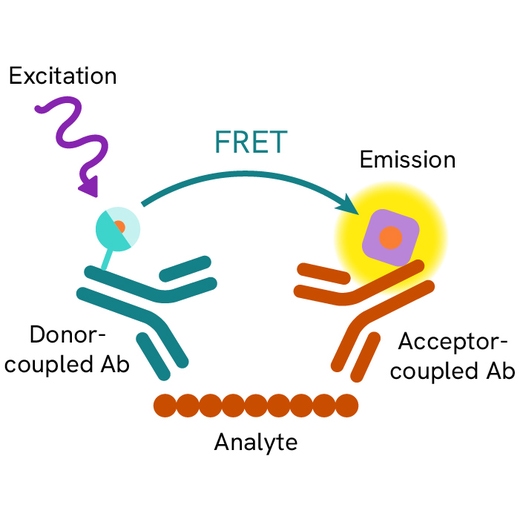
Assay principle

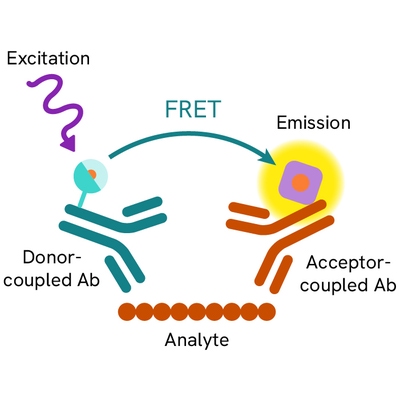
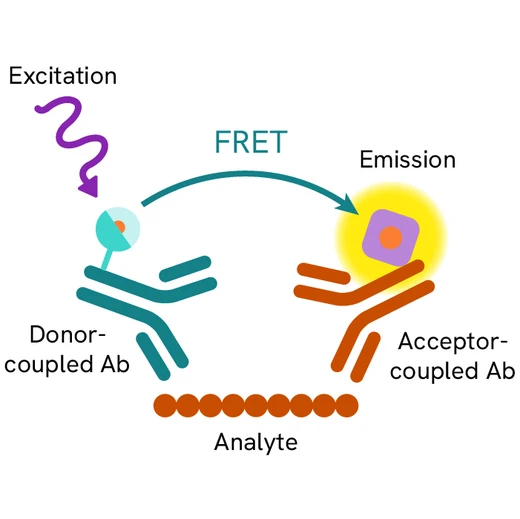
The cleaved-PARP assay is a sandwich immunoassay using two specific anti-PARP-1 p85 fragment monoclonal antibodies, one labelled with Eu3+ Cryptate (donor) and the other with d2 (acceptor). Donor-acceptor proximity leads to a fluorescent TR-FRET signal proportional to the number of cells undergoing apoptosis. The protocol is optimized for a 384-well plate format, but can easily be further miniaturized or upscaled. After cell lysis, the cleaved PARP-1 p85 fragment can be semi-quantitatively detected using the HTRF cleaved-PARP-Asp214 assay kit reagents.
Assay protocol
Two-plate assay protocol For added flexibility, the assay can be run under a two-plate assay protocol, where cells are plated and treated in a 96-well culture plate. For detection, lysates are subsequently transferred to a 384-well sv assay plate where the detection reagents are added. The detection reagents may be pre-mixed and added in a single dispensing step for direct detection. No washing is needed at any step. This also enables monitoring of the cells' viability and confluence in an appropriate cell culture plate.

Assay validation
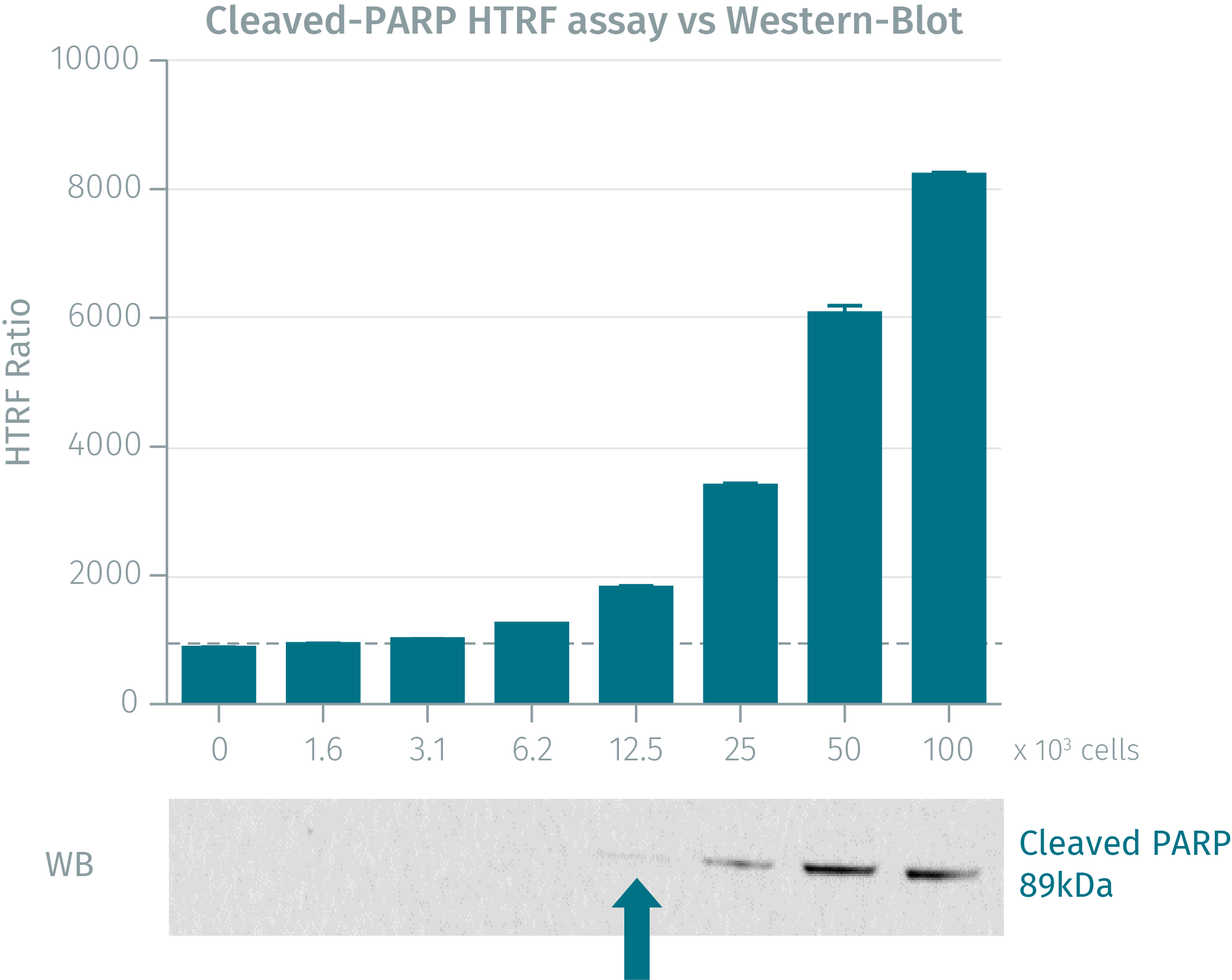
HTRF assay compared to Western Blot
Jurkat cells were grown in a T175 flask at 37°C - 5% CO2, and then stimulated for 4 hours with staurosporine. After centrifugation and medium removal, pelleted cells were lysed with 3 mL of supplemented lysis buffer for 30 min at RT. Soluble fractions were then collected after a 10 min centrifugation. Serial dilutions of the cell lysate were performed in the supplemented lysis buffer and 16 µL of each dilution were dispensed and analyzed side-by-side by Western Blot and by HTRF. Using the HTRF cleaved PARP Asp214 cellular assay, just 3,125 cells were sufficient for minimal signal detection whereas 12,500 cells were needed for a Western Blot signal. The HTRF cellular assay displays a better sensitivity than Western Blot.
Cleaved PARP-1 detection on Staurosporine treated HeLa cells
50,000 human cervical cancer HeLa cells were plated in 96-well plates and incubated for 24h at 37°C - 5% CO2. After incubating with increasing concentrations of Staurosporine for 4 hours, the medium was removed and cells were lysed with 50 µL of lysis buffer for 30 min at RT under gentle shaking. 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well sv white microplate, and 4 µL of the HTRF Cleaved PARP Asp214 detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after a 2h incubation time.

Cleaved PARP-1 detection on Staurosporine treated C2C12 cells
50,000 mouse myoblast cells were plated in 96-well plates and incubated for 24h at 37°C - 5% CO2. After incubating with increasing concentrations of Staurosporine for 4 hours, the medium was removed and cells were lysed with 50 µL of lysis buffer for 30 min at RT under gentle shaking. 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well sv white microplate, and 4 µL of the HTRF Cleaved PARP Asp214 detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after a 2h incubation time.

Simplified pathway
Cleaved PARP pathway
Two pathways activate the effector pro-caspase 3 that cleaved PARP on Asp214, leading to apoptosis:
- an extrinsic pathway (activated by death ligands like TNF alpha, FasL and ApoL that bind to their death receptors), activating the initiator procaspase-8
- an intrinsic pathway, or mitochondrial pathway (activated by cellular damage like stress, radiation, toxins, hypoxia and growth factor withdrawal), also activating pro-apoptotic factors like BAD, then the initiator procaspase-9
In response to death ligands or cell damage and activation of extrinsic or intrinsic apoptosis pathways, the nuclear enzyme PARP-1 (116 kDa) involved in the repair of damaged DNA is cleaved between Asp214 and Gly215 by activated caspases 3 and 7. The cleavage deactivates the enzyme by separating its N-terminal DNA binding domain p25 (24kDa) from its C-terminal catalytic domain p85 (89kDa), leading to DNA fragmentation and cell apoptosis. Cleaved PARP-1 is considered as an essential marker of apoptosis.

Specifications
| Application |
Protein Quantification
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
16 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target Class |
Biomarkers
|
| Target Species |
Human
Mouse
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Cardiovascular
Infectious Diseases
Metabolism/Diabetes
NASH/Fibrosis
Neuroscience
Rare Diseases
|
| Unit Size |
500 assay points
|
Video gallery
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
Discover the versatility and precision of Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF) technology. Our HTRF portfolio offers a...
This guide provides you an overview of HTRF applications in several therapeutic areas.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has transformed the field of immuno-oncology providing a novel approach to treating...


Loading...
How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.