HTRF Human Phospho-p53 (Ser15) Detection Kit, 96 Assay Points





The phospho-p53 (Ser15) kit enables the cell-based quantitative detection of phosphorylated p53 as a readout of the stress signaling pathway.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Cell Signaling |
| Sample Volume | 16 µL |
The phospho-p53 (Ser15) kit enables the cell-based quantitative detection of phosphorylated p53 as a readout of the stress signaling pathway.









Product information
Overview
This HTRF cell based assay conveniently and accurately quantifies phosphorylated p53 at Ser15. P53 has been described as the guardian of the genome because of its role in safeguarding genome integrity. P53 has many anticancer function mechanisms, influencing apoptosis, senescence, cell cycle regulation, growth arrest, genomic stability, angiogenesis inhibition, and metabolism changes, by regulating the expression of various target genes.
HTRF assays offer many advantages over other technologies:
- Homogeneous add-and-read format
- No wash steps
- Low background
- Straightforward miniaturization from 96- or 384-well microplates to high density assay formats such as 384-well low volume and 1536-well plates
- Stable signal, providing flexibility in time of readout or size of assays
How it works
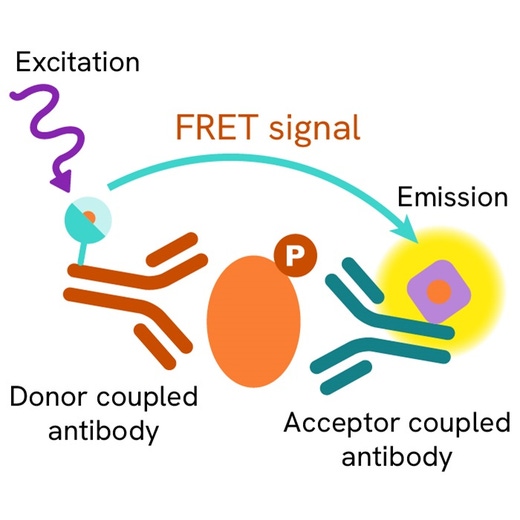
Phospho-p53 (Ser15) assay principle
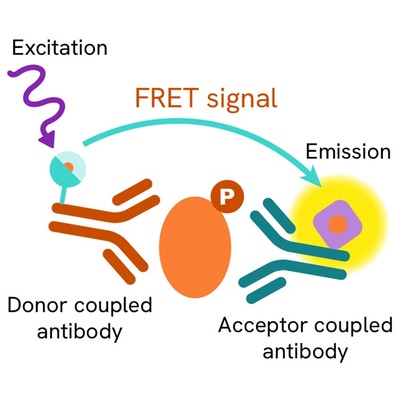
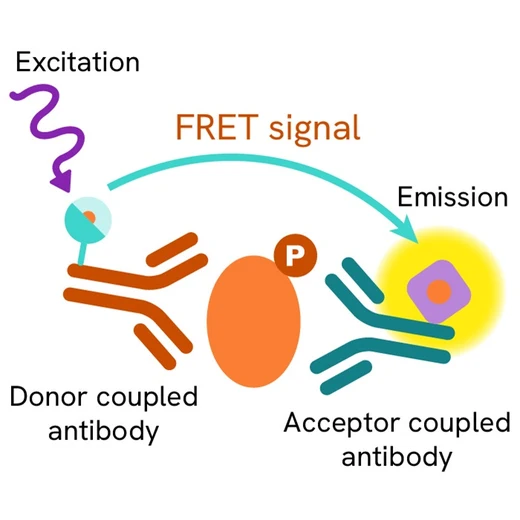
The Phospho-p53 (Ser15) assay measures p53 when phosphorylated at Ser15. Contrary to Western Blot, the assay is entirely plate-based and does not require gels, electrophoresis or transfer. The Phospho-p53 (Ser15) assay uses 2 labeled antibodies: one with a donor fluorophore, the other one with an acceptor. The first antibody is selected for its specific binding to the phosphorylated motif on the protein, the second for its ability to recognize the protein independent of its phosphorylation state. Protein phosphorylation enables an immune-complex formation involving both labeled antibodies and which brings the donor fluorophore into close proximity to the acceptor, thereby generating a FRET signal. Its intensity is directly proportional to the concentration of phosphorylated protein present in the sample, and provides a means of assessing the proteins phosphorylation state under a no-wash assay format.

Phospho-p53 (Ser15) 2-plate assay protocol
The 2 plate protocol involves culturing cells in a 96-well plate before lysis then transferring lysates to a 384-well low volume detection plate before adding Phospho-p53 (Ser15) HTRF detection reagents. This protocol enables the cells' viability and confluence to be monitored.

Phospho-p53 (Ser15) 1-plate assay protocol
Detection of Phosphorylated p53 (Ser15) with HTRF reagents can be performed in a single plate used for culturing, stimulation and lysis. No washing steps are required. This HTS designed protocol enables miniaturization while maintaining robust HTRF quality.

Assay validation
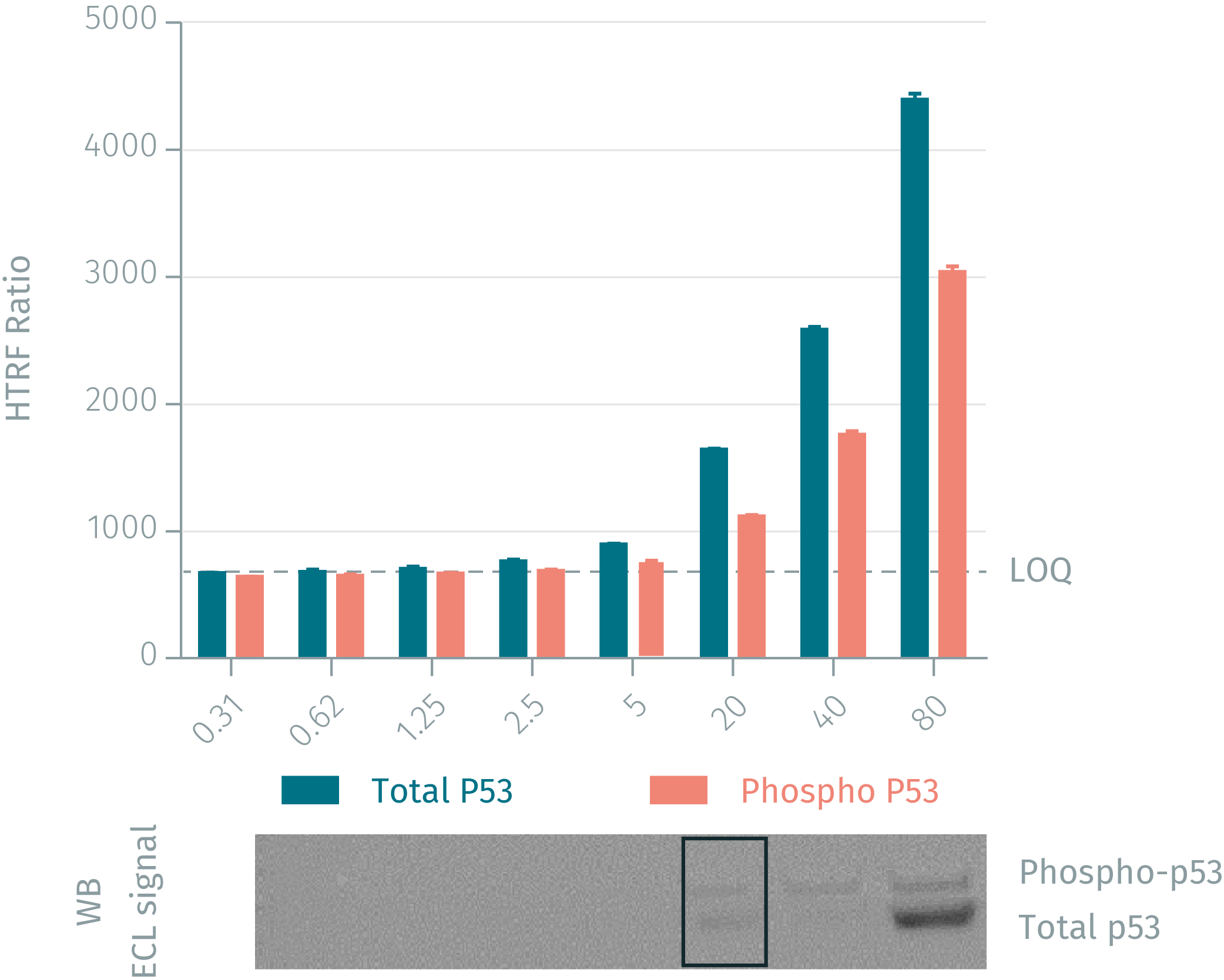
HTRF assay vs WB using Phospho & total P53 assays on human MCF-7 cells
Human MCF-7 cells were plated at 106 cells/ well in a 6 well plate, and incubated for 24h at 37°C, 5% CO2. After treatment for 5 min under UV (2.1J/cm²), the cells were lysed with 200 µL of lysis buffer for 30min at RT under gentle shaking. Serial dilutions of the cell lysate were performed in the supplemented lysis buffer and 16 µL of each dilution were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate before the addition of 4 µL of the HTRF phospho-p53 (Ser15) detection reagents. Equal amounts of lysates were used for a side by side comparison of Western Blot and HTRF. Results show that the two HTRF p-53 assays are at least 4-fold more sensitive than the Western Blot.
Validation on Neocarcinostatin treated MCF-7 breast cancer cells
Human MCF-7 cells were plated at 100,000 cells/ well in a 96 well plate, and incubated for 24h at 37°C, 5% CO2. After treatment for 45 min with increasing concentrations of Neocarcinostatin, the medium was removed and the cells were lysed with 50 µL of lysis buffer for 30min at RT under gentle shaking. 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate and 4 µL of the HTRF phospho-p53 (Ser15) or total p53 detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation.

Validation on Etoposide (apoptosis inductor) treated breast cancer MCF-7 cells
Human MCF-7 cells were plated at 200,000 cells/ well in a 96 well plate, and incubated for 24h at 37°C, 5% CO2. After treatment for 3 h with increasing concentrations of Etoposide, the medium was then removed and the cells were lysed with 50 µL of lysis buffer for 30min at RT under gentle shaking. 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate and 4 µL of the HTRF phospho-p53 (Ser15) or total p53 detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation.

Simplified pathway
Function and regulation of p53
P53 becomes activated by a myriad of stressors including, but not limited to, DNA damage, oxidative stress, osmotic shock, ribonucleotide depletion, and deregulated oncogene expression. In response to such stresses, p53 undergoes extensive posttranslational modifications, including phosphorylation and acetylation. Phosphorylation of p53 mostly occurs in the N-terminal at Ser15 and leads to a reduced interaction between p53 and its negative regulator, the oncoprotein MDM2, which inhibits p53 accumulation by targeting it for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Phosphorylation in this site impairs the ability of MDM2 to bind p53, promoting both the accumulation and activation of p53 in response to DNA damage.

Specifications
| Application |
Cell Signaling
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Lysis Buffer Compatibility |
Lysis Buffer 1
|
| Molecular Modification |
Phosphorylation
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
16 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target Class |
Phosphoproteins
|
| Target Species |
Human
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Oncology & Inflammation
|
| Unit Size |
96 assay points
|
Video gallery
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
This guide provides you an overview of HTRF applications in several therapeutic areas.
An in-depth review of molecular and cellular pathways
The maintenance of proteostasis, the biological mechanisms that control the...


Loading...
How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.