HTRF EPIgeneous Binding Domain B Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points





| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Biochemical Enzymatic Assay |
| Sample Volume | 120 µL |









Product information
Overview
The EPIgeneous Binding Domain kit series provides a simple biochemical approach to study epigenetic reader domain interactions with modified histones. All kits are based on a GST-tagged binding domain / biotin-coupled Histone peptide format, and can be run using the same add-and-read single plate protocol.
Binding Domain kit B has been successfully validated on a wide variety of readers (18), including some important therapeutic epigenetic targets.
How it works
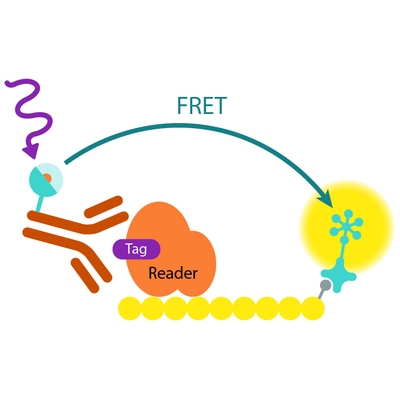
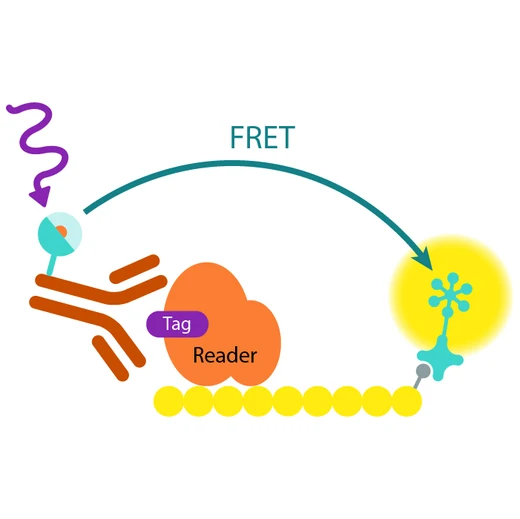
Assay principle
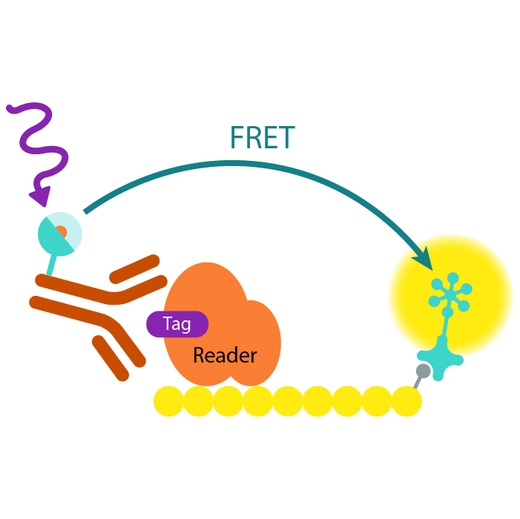
In EPIgeneous Binding Domain kit B, the GST-tagged reader domain protein binding to the biotinylated peptide substrate is detected by a conjugate mix: anti-GST Eu cryptate-labeled antibody conjugate (donor), and XL665-conjugated streptavidin (acceptor). The interaction of the reader domain with the substrate brings the donor and acceptor dyes into close proximity, and allows FRET to occur upon light excitation. The specific signal at 665 nm is inhibited when a specific compound prevents the reader domain protein from binding to its substrate.

Analytical performance
Peptide-biotin titration - UHRF1/ histone H3 peptide interaction
The validation of the EPIgeneous binding Domain B assay was performed using the Tudor Domain UHRF1 binding to [Lys(9)Me3] H3(1-21) peptide. The GST-UHRF1 concentration was fixed at 5 nM while the peptide-biotin was serially diluted.
The HTRF signal was proportional to the specific interaction measured between GST-UHRF1 and peptide-biotin.
The 2nM Kd value was determined from this experiment using a two-site specific binding regression. A slight shift of apparent Kd is observed when DMSO% increases.

DMSO tolerance - peptide-biotin concentration optimization
The assay window slightly decreased as the DMSO percentage increased. The assay window could then be recovered by increasing the peptide-biotin concentration. The optimal peptide-biotin concentration was selected (between real Kd and EC100 obtained on the titration without DMSO) with a compromise between assay window and assay sensitivity for inhibitor studies. Note that the higher the peptide-biotin concentration, the higher the inhibitor IC50. For further study of inhibitors, 1% DMSO and 6nM peptide-biotin conditions were applied.

Inhibitor titration - UHRF1 by reference compound
The EPIgeneous Binding Domain B assay was performed using 4 nM peptide-biotin, 5 nM GST-UHRF1 and 1% DMSO set constant throughout the inhibitor titration. The IC50 of [Lys(9)Me3]-H3(1-21) peptide is in good agreement with published data (Rothbart et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2012 - 2µM)

Assay validation
Validated binding domains
Three kits (A, B and C) have already been validated and fully optimized on a selection of 28 key binding domains. For non-validated reader domains, a fourth one, the Discovery Kit, enables researchers to profile which of the A, B or C kits is the best assay solution.

| BINDING DOMAIN KIT A | BINDING DOMAIN KIT B | BINDING DOMAIN KIT C |
|---|---|---|
| BRD2(1) | CECR2 | BRD4(1/2) |
| BRD3(1) | FALZ (BPTF) | ATAD2A |
| BRD4(1) | BRD2(2) | ATAD2B |
| CBX 1 | BRD2(1/2) | BRD9 |
| BRD3(2) | SMARCA4 (BRG1) | |
| BRD3(1/2) | BAZ2B | |
| BRD4(2) | ||
| BRDT(1) | ||
| BRDT(1/2) | ||
| CREBBP | ||
| BRD1 | ||
| BRPF3 | ||
| TAF1L(2) | ||
| TAF1L(1/2) | ||
| TAF1(2) | ||
| TAF1(1/2) | ||
| L3MBTL1 | ||
| UHRF1 |
Specifications
| Application |
Biochemical Enzymatic Assay
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
EPIgeneous
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
120 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target Class |
Epigenetics
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Metabolism/Diabetes
Neuroscience
Oncology & Inflammation
|
| Unit Size |
500 assay points
|
Video gallery
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
Discover the versatility and precision of Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF) technology. Our HTRF portfolio offers a...
This guide provides you an overview of HTRF applications in several therapeutic areas.


Loading...
How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.