HTRF Human and Mouse Total TDP-43 Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points





This HTRF kit enables the cell-based quantitative detection of total TDP43.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Cell Signaling |
| Sample Volume | 16 µL |
This HTRF kit enables the cell-based quantitative detection of total TDP43.









Product information
Overview
TAR DNA binding protein 43 (TDP-43) is a nucleic acid binding protein involved in RNA-related metabolism. Aggregated TDP-43 has been identified as a hallmark of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal lobar dementia (FTLD), and more widely in several neurodegenerative diseases: TDP-43 proteinopathies. In pathological conditions (mutation or dysregulation), TDP-43 forms insoluble inclusion bodies in the cytoplasm of neurons in the brain and spinal cord. The TDP-43 Phospho-Ser409/410 assay detects human TDP-43 phosphorylated in cell lysates.
How it works
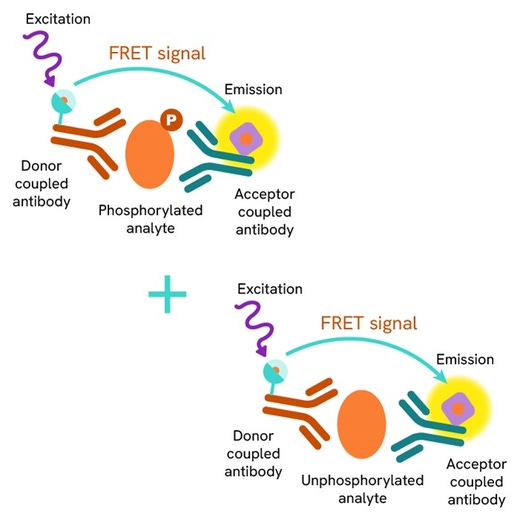
Total TDP-43 assay principle
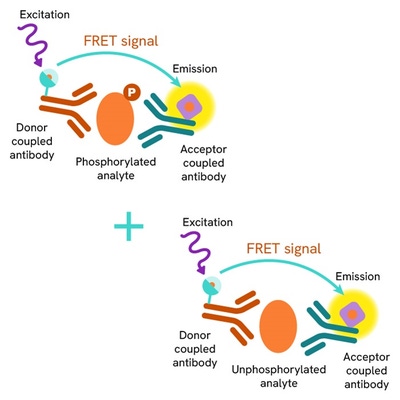
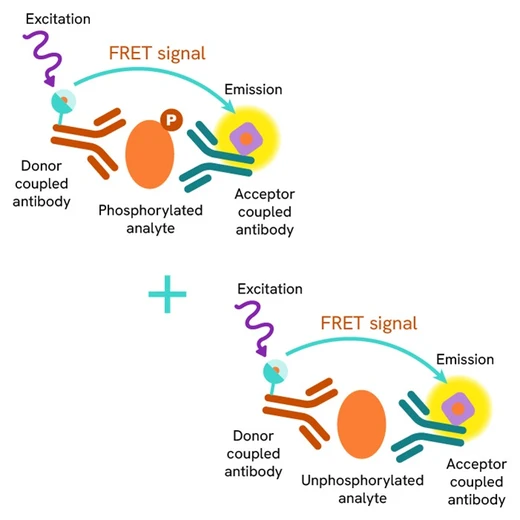
The HTRF Total TDP-43 assay quantifies the expression level of TDP-43 in a cell lysate. Unlike Western Blot, the assay is entirely plate-based and does not require gels, electrophoresis, or transfer. The Total TDP-43 assay uses two labeled antibodies, one coupled to a donor fluorophore, the other to an acceptor. Both antibodies are highly specific for a distinct epitope on the protein. In presence of TDP-43 in a cell extract, the addition of these conjugates brings the donor fluorophore into close proximity with the acceptor, and thereby generates a FRET signal. Its intensity is directly proportional to the concentration of the protein present in the sample, and provides a means of assessing the protein’s expression under a no-wash assay format.

Total TDP-43 two-plate assay protocol
The two-plate protocol involves culturing cells in a 96-well plate before lysis, then transferring lysates to a 384-well low volume detection plate before the addition of the Total TDP-43 HTRF detection reagents. This protocol enables the cells' viability and confluence to be monitored.

Total TDP-43 one-plate assay protocol
Detection of Total TDP-43 with HTRF reagents can be performed in a single plate used for culturing, stimulation, and lysis. No washing steps are required. This HTS-designed protocol enables miniaturization while maintaining robust HTRF quality.

Assay validation
Phospho-TDP-43 (Ser409/410) modulation using Calyculin A
Neuro2a cells were cultured in a 96-well plate (50,000 cells/well) for 24h and then treated for 30 min with increasing concentrations of Calyculin A (protein phosphatase 1 and 2A inhibitor). After treatment, cells were lysed with 10 µL of supplemented lysis buffer #1 (4X) for 30 min at room temperature under gentle shaking (as per the suspension cell protocol).
After lysis, 16 µL of lysates were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate, and 4 µL of the HTRF Phospho-TDP-43 (Ser409/410) or Total TDP-43 detection antibodies were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation at room temperature.
As expected, Calyculin A triggered a dose-dependent accumulation of phosphorylated TDP-43 at Ser409/410 through inhibition of PP1/2, while the expression level of the protein was not modulated by the treatment.

Inhibition of Phospho-TDP-43 (Ser409/410) / Total TDP-43 with CK1 inhibitors
Neuro2a cells were cultured in a 96-well plate (50,000 cells/well) for 24h, and then treated for 1h30 with the Casein Kinase 1 (CK1) inhibitors IC 261 or PF 670462 (100 µM), followed by Calyculin A activation (30 min, 100 nM).
After cell lysis, 16 µL of lysates were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate and 4 µL of the HTRF Phospho-TDP-43 (Ser409/410) or Total TDP-43 detection antibodies were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation.
As expected, the results obtained showed an inhibition of TDP-43 Ser409/410, triggered by Calyculin A after CK1 inhibitor treatment, while the expression level of the protein was not modulated by the treatment.

Assessment of Total TDP-43 levels in various cell lines
Adherent human & mouse cells Neuro 2A, HeLa, and SH-SY5Y were seeded at 50,000 cells/well in a 96-well microplate. After a 24h incubation, the cells were lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer #1 (1X) for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking.
Following lysis, 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate before the addition of 4 µL of the HTRF Total TDP-43 detection reagents. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation.
The HTRF Total TDP-43 assay efficiently detected total TDP-43 in various human and mouse cell models with different expression levels.

HTRF Total TDP-43 assay compared to Western Blot
HeLa cells were cultured in a T175 flask in complete culture medium at 37°C, 5% CO2. After a 48h incubation, the cells were treated with Calyculin A (30 min, 100 nM), then lysed with 3 mL of supplemented lysis buffer #1 (1X) for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking.
Serial dilutions of the cell lysate were performed using supplemented lysis buffer, and 16 µL of each dilution were transferred into a low volume white microplate before the addition of 4 µL of HTRF Total TDP-43 detection reagents. Equal amounts of lysates were used for a side-by-side comparison between HTRF and Western Blot.
Using the HTRF Total TDP-43 assay, 1,000 cells/well were enough to detect a significant signal, while 4,000 cells were needed to obtain a minimal chemiluminescent signal using Western Blot. Therefore in these conditions, the HTRF Total TDP-43 assay was 4 times more sensitive than the Western Blot technique.

Simplified pathway
TDP-43 Signaling Pathway
TDP-43 (TAR DNA binding protein 43) is a DNA and RNA-binding protein which plays a crucial role in RNA metabolism. Mainly located in the nucleus, TDP-43 shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
The phosphorylation of TDP-43 is regulated, even if it can be an aberrant process in pathological conditions. Several kinases, including Casein Kinases (CK1 & 2), Tau Tubulin Kinases (TTBK 1 & 2) and cell division cycle 7 (CDC7), are known to promote TDP-43 phosphorylation, whereas phosphatases (PP1 &2) and Calcineurin catalyze its dephosphorylation. Dysregulation of these processes by some mutations, oxidative stress, etc. may lead to an increase in TDP-43 phosphorylation. The phosphorylation of TDP-43 impacts cell functions such as RNA binding or alternative splicing, and induces a mislocalization and accumulation in the cytoplasm, triggering aggregate formation.
In pathological conditions, phospho-TDP-43 Ser409/410 is a hallmark of proteinopathies such as Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), FrontoTemporal Dementia (FTD), or Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). Aberrant phosphorylation, cytoplasmic accumulation, and aggregation of TDP-43 impair the clearance through the proteasome and autophagy mechanisms, leading to neuron cell toxicity.
TDP-43 phosphorylation and its regulation may provide new therapeutic directions to treat neurodegenenerative diseases.

Specifications
| Application |
Cell Signaling
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Lysis Buffer Compatibility |
Lysis Buffer 1
Lysis Buffer 2
Lysis Buffer 3
Lysis Buffer 4
|
| Molecular Modification |
Total
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
16 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target Class |
Phosphoproteins
|
| Target Species |
Human
Mouse
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Unit Size |
500 assay points
|
Video gallery
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
Discover the versatility and precision of Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF) technology. Our HTRF portfolio offers a...


Loading...
How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.