IVIS Lumina LT In Vivo Imaging System
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Part #:
CLS136331
Imaging Modality:
2D Bioluminescence, 2D Fluorescence
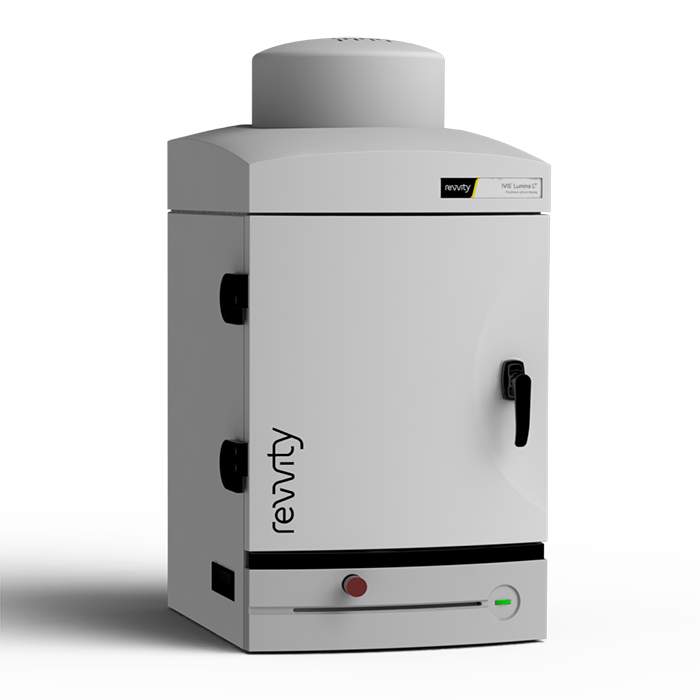

IVIS Lumina LT In Vivo Imaging System
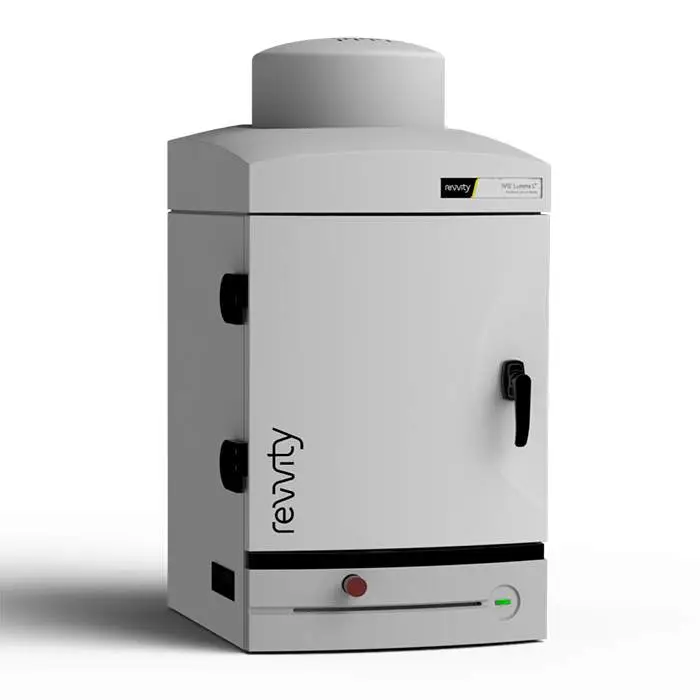

IVIS Lumina Series III benchtop 2D optical imaging system
IVIS Lumina LT In Vivo Imaging System

Product information
Overview
The IVIS Lumina LT optical imaging system is equipped with 2D bioluminescence, fluorescence, and radioisoptic (Cerenkov) imaging capabilities. For more sophisticated fluorescent models, the IVIS Lumina LT can be easily upgraded to an IVIS Lumina III system offering users enhanced fluorescence imaging tunability for improved sensitivity from the visible to near infrared imaging spectrum.
Features/Benefits:
- 2D Bioluminescence
- 2D Fluorescence
- Radioisotopic Cerenkov Imaging
- Compute Pure Spectrum Spectral Unmixing
- DyCE Imaging (Optional Upgrade)
- Extended NIR Range 150W Tungsten EKE
- Absolute Calibration to NIST® Standards
- Complimentary Living Image™ software licenses are provided with the IVIS systems and upon request.
Specifications
| Dimensions | 48.0 cm (W) x 104.0 cm (H) |
|---|
| Brand |
IVIS
|
|---|---|
| Imaging Modality |
2D Bioluminescence
2D Fluorescence
|
| Unit Size |
1 unit
|
References
- Wang et al (2021). LncRNA SPOCD1-AS from ovarian cancer extracellular vesicles remodels mesothelial cells to promote peritoneal metastasis via interacting with G3BP1. J Exp & Clin Res. 40(101). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-021-01899-6
- Zhong et al (2021). Calcium phosphate engineered photosynthetic microalgae to combat hypoxic-tumor by in-situ modulating hypoxia and cascade radio-phototherapy. Thernostics. 11(8): 3580–3594. https://dx.doi.org/10.7150%2Fthno.55441
- Li et al (2020). High selective distinguishable detection GSH and H2S based on steric configuration of molecular in Vivo. Dyes & Pigments. 172;107826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2019.107826
- Korolev et al (2020). Fluorescent Nanoagents for Biomedical Applications. Fluorescence Methods for Investigation of Living Cells and Microorganisms. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.92904
- Zhai et al (2020). An ATF24 peptide-functionalized β-elemene-nanostructured lipid carrier combined with cisplatin for bladder cancer treatment. Cancer Biol & Med. 17(3): 676–692. https://dx.doi.org/10.20892%2Fj.issn.2095-3941.2020.0454
- Natoni et al (2020). Sialyltransferase inhibition leads to inhibition of tumor cell interactions with E-selectin, VCAM1, and MADCAM1, and improves survival in a human multiple myeloma mouse model. Haematologia. 105(2): 457–467. https://dx.doi.org/10.3324%2Fhaematol.2018.212266
- Costa et al (2019). Murine infection with bioluminescent Leishmania infantum axenic amastigotes applied to drug discovery. Sci Reports. 9: 18989. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-55474-3
- Ramachandran et al (2019). Non-invasive in vivo imaging of fluorescence-labeled bacterial distributions in aquatic species. Internat'l J Vet Sci Med. 5(2). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijvsm.2017.09.003
- Song et al (2019). Overcoming hypoxia-induced chemoresistance to cisplatin through tumor oxygenation monitored by optical imaging. Nanothernostics. 3(2): 223–235. https://dx.doi.org/10.7150%2Fntno.35935
- Lorscheider et al (2019). Dexamethasone palmitate nanoparticles: An efficient treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. J Controlled Rel. 296:179-189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.01.015
- Lazzari et al (2018). Multicellular spheroid based on a triple co-culture: A novel 3D model to mimic pancreatic tumor complexity. Acta Biomaterials. 78: 296-307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2018.08.008
- Cayre et al (2017). In Vivo FRET Imaging to Predict the Risk Associated with Hepatic Accumulation of Squalene‐Based Prodrug Nanoparticles. Adv. Healthcare Mat. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201700830
Citations
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.