POPOP Scintillator, 5 g




| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Grade | Scintillator |
| Molecular Weight | 364.40 g/mol |
| CAS Number | 1806-34-4 |
| Maximum Emission Wavelength (Emmax) | ~420 nm |
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.












Loading...
Product information
Overview
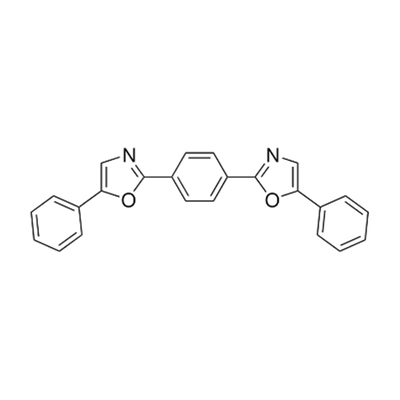
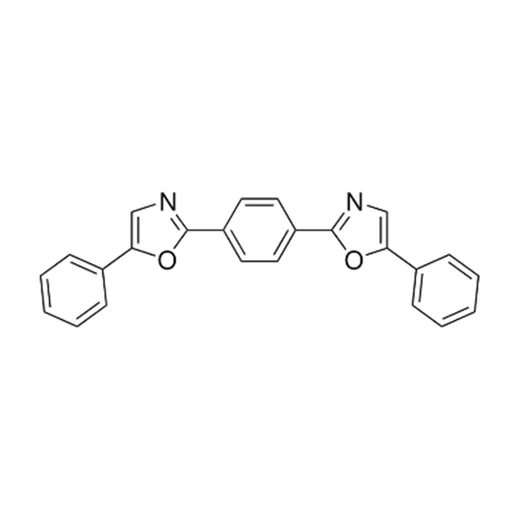
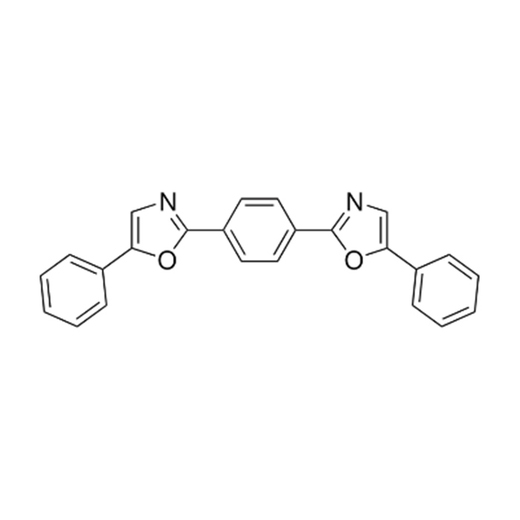
POPOP, IUPAC preferred name 5-phenyl-2-[4-(5-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-2-yl)phenyl]-1,3-oxazol, has an aromatic ring structure fundamental for fluorescent properties.
POPOP is a secondary scintillator or wavelength shifter and converts shorter wavelength light to longer wavelength light that can be detected by liquid scintillation analyzers (LSA) such as a TriCarb or Quantulus GCT.
The structure of the POPOP molecule is a central benzene ring containing two oxazolyl groups each having a phenyl ring. The conjugated aromatic property of POPOP contributes to its fluorescence and ability to act as a wavelength shifter. POPOP fluoresces as a blue-violet color with excitation wavelength of ~ 360 nm and an emission wavelength of ~420 nm. The exact fluorescence maximum can vary slightly depending on the solvent used.
The molecular formula of POPOP is C24H16N2O2, a melting point of 241-243°C and a fluorescence maximum of 425 nm.
Specifications
| Maximum Emission Wavelength (Emmax) |
~420 nm
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
364.40 g/mol
|
| CAS Number |
1806-34-4
|
| Application |
Liquid scintillation counting
|
|---|---|
| Detection Modality |
Radiometric
|
| Format |
Powder
|
| Grade |
Scintillator
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped Ambient
|
| Unit Size |
1 x 5 g
|
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.