
AlphaLISA Human Amyloid-β 1-40 Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points
 View All
View All







| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Protein Quantification |
| Dynamic Range | 87.9 - 100,000 pg/mL |
| Limit of Detection | 87.9 pg/mL |
| Sample Volume | 5 µL |















Product information
Overview
One antibody is specific to amino acids 17-24 (epitope VFFAE): mouse monoclonal antibody, clone number 4G8. The second antibody is specific to the C-terminus: mouse monoclonal antibody, clone number 11A50-B10.
Formats:
- Our 500 assay point kit allows you to run 500 wells in 96-well or 384-well format, using a 50 µL reaction volume (5 µL of sample).
- Our 5,000 assay point kit allows you to run 5,000 wells in 96-well or 384-well format, using a 50 µL reaction volume (5 µL of sample).
Features:
- No-wash steps, no separation steps
- ELISA alternative technology
- Sensitive detection
- Broad sample compatibility
- Small sample volume
- Results in less than 3 hours
- Half the time of an ELISA assay
Amyloid beta (Aß) is a short peptide derived from the proteolysis of a larger transmembrane molecule, the amyloid precursor protein (APP). The ß- and γ-secretases cleave the respective N- and C-terminal ends of the Aß sequence, liberating the Aß peptide from APP. Aß40 is the major species of Aß produced by neurons and other cells, and accounts for over 70% of total Aß produced, while the remaining 10-20% is comprised of the longer Aß42, and other species. Aß42 has a greater propensity to form aggregates or fibrils and also has a greater neuronal toxicity in tissue culture models than Aß40, implying that Aß42 is a more important factor in Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis and plaque formation. Levels of Aß42 in cerebrospinal fluid are decreased in the majority of AD subjects (probably due to its aggregation into plaques), making it an important biomarker for this disease.
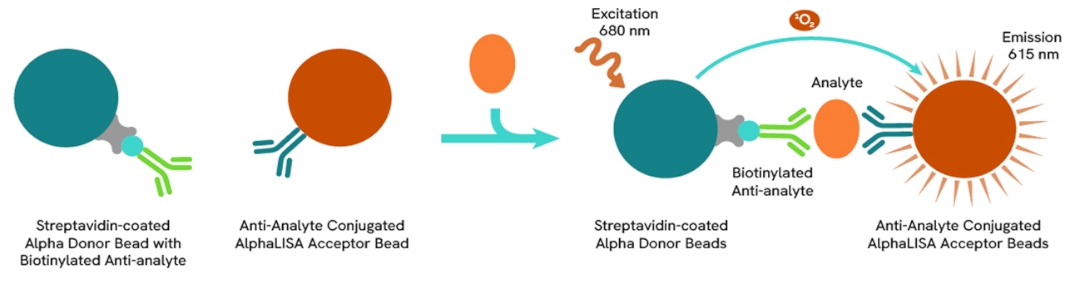
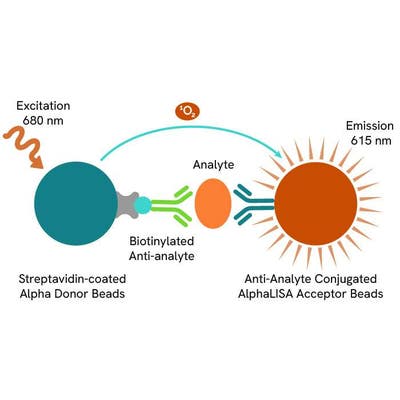
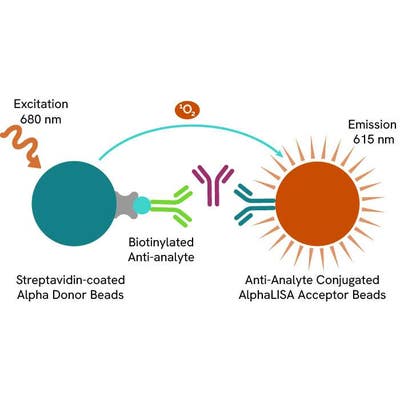
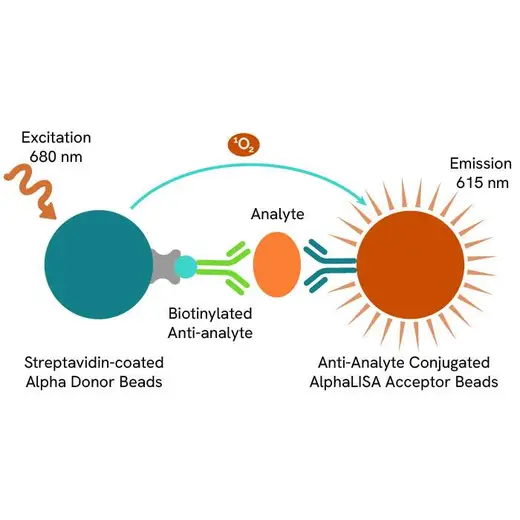
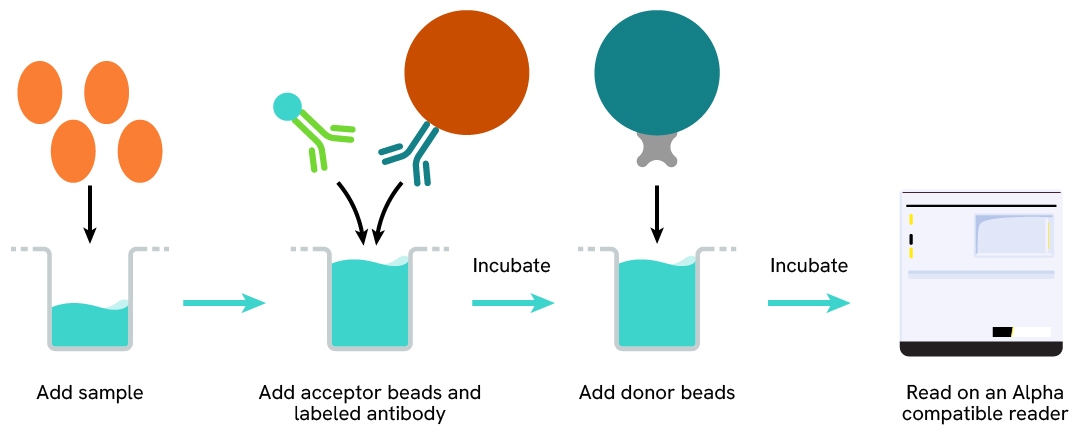
AlphaLISA technology allows the detection of molecules of interest in a no-wash, highly sensitive, quantitative assay. In an AlphaLISA assay, a biotinylated anti-analyte antibody binds to the Streptavidin-coated Donor beads while another anti-analyte antibody is conjugated to AlphaLISA Acceptor beads. In the presence of the analyte, the beads come into close proximity. The excitation of the Donor beads causes the release of singlet oxygen molecules that triggers a cascade of energy transfer in the Acceptor beads, resulting in a sharp peak of light emission at 615 nm.
How it works
Principle of the AlphaLISA assay
The AlphaLISA assay is based on an AlphaLISA sandwich immunoassay involving a biotinylated anti-analyte antibody bound to Streptavidin-coated AlphaLISA Donor beads and an anti-analyte antibody conjugated to AlphaLISA Acceptor beads. Both antibodies are directed against the analyte of interest. In the presence of the target, both antibodies bind to analyte and the beads come into proximity. The excitation of the Donor beads provokes the release of singlet oxygen molecules that triggers a cascade of energy transfer within the Acceptor beads, resulting in emission with λmax at 615 nm. The intensity of the signal is directly proportional to the concentration of analyte present in the sample.

Protocol of the AlphaLISA assay
The AlphaLISA assay can be run in a 96- or 384-well detection plate (50 µL final). As described here, samples or standards are dispensed directly into the assay plate for the detection of the analyte of interest by AlphaLISA reagents. No washing steps are needed. The protocol can be further miniaturized or upscaled by simply resizing each addition volume proportionally.
Specifications
| Application |
Protein Quantification
|
|---|---|
| Automation Compatible |
Yes
|
| Brand |
AlphaLISA
|
| Detection Modality |
Alpha
|
| Dynamic Range |
87.9 - 100,000 pg/mL
|
| Host Species |
Mouse
|
| Limit of Detection |
87.9 pg/mL
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
5 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Blue Ice
|
| Target |
Aβ40
|
| Target Class |
Biomarkers
|
| Target Species |
Human
|
| Technology |
Alpha
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Central Nervous System
|
| Unit Size |
500 assay points
|
Video gallery
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.


Loading...
How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.