
NEXTFLEX Cas9-gRNA Mito Depletion Enzyme (Human)



| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Automation Compatible | Yes |
| Product Group | RNA Depletion |



Product information
Overview
Mitochondrial-derived fragments can account for a large share of reads in human ATAC-seq, DNA-seq, and bulk or single cell RNA-seq libraries, especially from mitochondria-rich tissues, reducing effective coverage of nuclear loci and low-abundance features. The NEXTFLEX Cas9-gRNA Mito Depletion Enzyme (Human) is a cost-effective, workflow-independent, and highly specific enzyme that reduces mitochondrial background, directing more sequencing capacity toward nuclear genes, regulatory elements, and other regions of interest, without requiring you to move to a new library prep kit.
It uses a DASH-style (Depletion of Abundant Sequences by Hybridization) CRISPR-Cas9 depletion approach, with a precomplexed Cas9 and pool of guides designed to cleave human mitochondrial DNA and selected nuclear mitochondrial pseudogenes at the double-stranded DNA stage. Whether you use your own prep method or a commercial kit, this module delivers clean, reproducible depletion of mitochondrial genome–derived sequences and improved coverage of nuclear content across diverse human NGS workflows.
- Powered by Jumpcode™ DepleteX™ technology for specific mitochondrial sequence removal
- Ready to use: provided as a Cas9-gRNA complex with integrated RNase inhibitor and 10X Cas9 Buffer
- Fast: one-hour reaction time with only about 5 minutes of hands-on work
- Convenient: easily fits into ATAC-seq, DNA-seq, RNA-seq, and single-cell workflows at the dsDNA stage
- Flexible: compatible with short- and long-read sequencing
- Automation-compatible: readily incorporated into manual or automated workflows
Additional product information
Cas9-gRNA-driven targeted mitochondrial depletion kit
The NEXTFLEX Cas9-gRNA Mito Depletion Enzyme (Human) is designed for datasets where mitochondrial reads stop being a minor annoyance and start consuming your experiment. In ATAC-seq, it removes the dominant mitochondrial peak that can soak up a large fraction of usable reads, sharpening nuclear open-chromatin profiles in mitochondria-rich tissues such as heart, muscle, or brain. In low-pass and whole-genome sequencing, it clears out the excess mitochondrial reads so more of your fixed sequencing budget is spent on nuclear chromosomes instead of mtDNA. For bulk and single-cell RNA-seq workflows, it cuts fragments derived from mitochondrial transcripts and mtDNA, reclaiming reads and redirecting them to nuclear genes that drive clustering, differential expression, and downstream biology. Because depletion occurs on double-stranded DNA, you can apply the enzyme either to amplified cDNA as part of a planned workflow or to completed libraries that turned out to be heavily mitochondrial, turning "high-mito" samples into usable data.

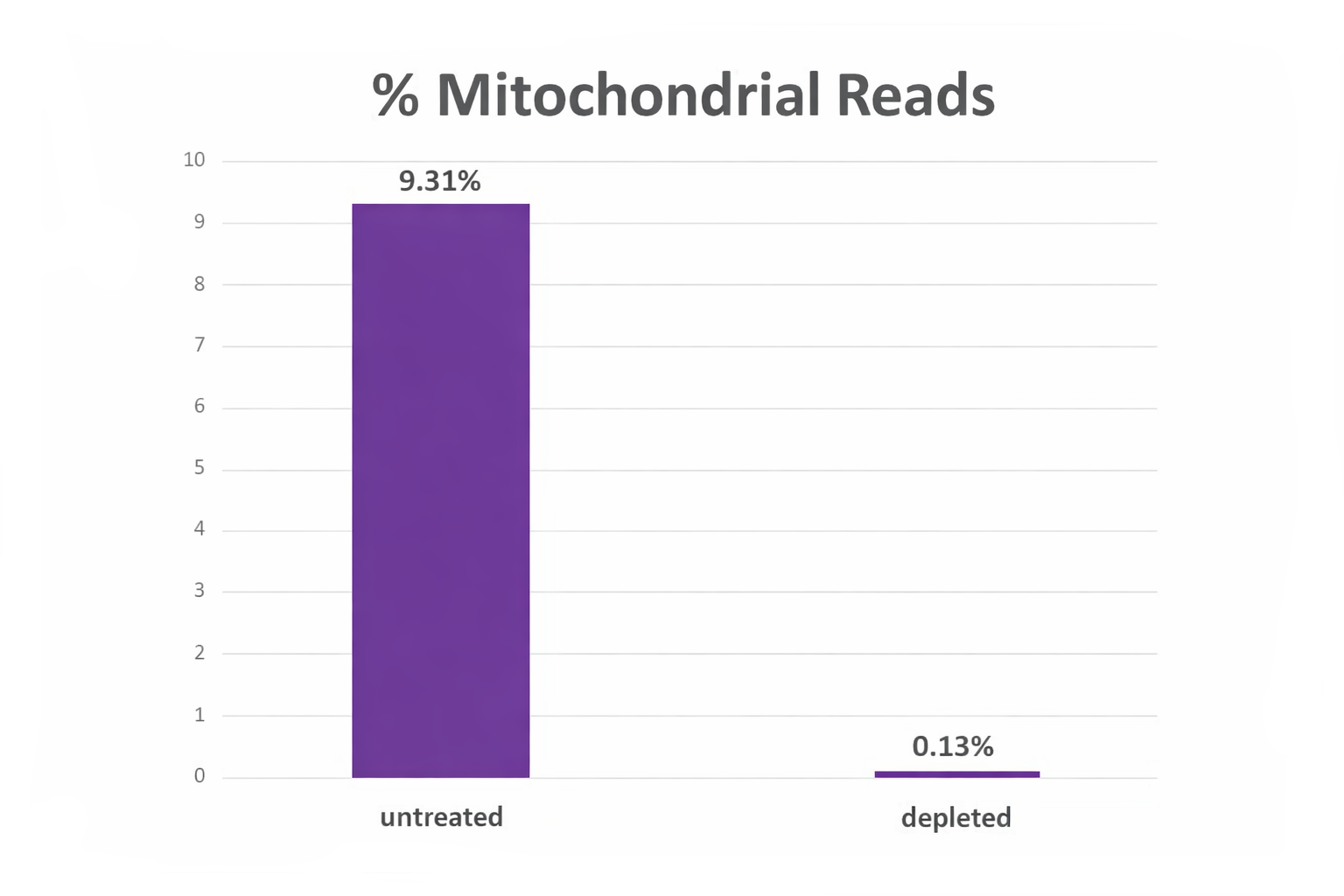
Figure 1. NEXTFLEX Cas9-gRNA Mito Depletion Enzyme (Human) dramatically reduces mitochondrial reads in NGS libraries obtained from a human tissue sample. Percent of reads mapped to the mitochondrial genome in an untreated library compared with the same library after depletion, showing a drop from 9.31% to 0.13% and freeing sequencing capacity for nuclear targets.
Mitochondrial depletion kit compatible with diverse human NGS workflows
Supplied as a standalone Cas9-gRNA complex rather than embedded in a specific library prep kit, the NEXTFLEX Cas9-gRNA Mito Depletion Enzyme (Human) can be added wherever your human samples have been converted to double-stranded DNA. You can introduce mitochondrial depletion into ATAC-seq, low-pass and whole-genome sequencing, targeted DNA panels, bulk, or single-cell RNA libraries without changing your upstream chemistry. Operating at the dsDNA stage avoids constraints around nucleic acid integrity or input type and keeps the module compatible with existing manual or automated workflows on both short- and long-read sequencing platforms.
Looking for an end-to-end NGS solution for mito depletion?
This mitochondrial depletion module works seamlessly with NEXTFLEX library prep solutions. Use NEXTFLEX kits to generate high quality DNA or RNA libraries from a broad range of inputs and sample qualities, then add the NEXTFLEX Cas9-gRNA Mito Depletion Enzyme (Human) to strip out mitochondrial background before sequencing. The result is a single, integrated workflow from sample to sequencing-ready library that increases the proportion of reads on nuclear targets and gives you one partner for chemistry, optimization, and technical support.
Specifications
| Automation Compatible |
Yes
|
|---|---|
| Product Group |
RNA Depletion
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Unit Size |
50 μL
|
FAQs
-
What are the benefits of using CRISPR-based mitochondrial depletion in DNA and RNA NGS libraries?
-
Why deplete mitochondrial genome–derived fragments at the dsDNA stage instead of at the RNA or genomic DNA stage?
-
Which species and sample types are supported for mitochondrial depletion?
-
What library prep kits and sequencing platforms are compatible with the NEXTFLEX Cas9-gRNA Mito Depletion Enzyme (Human)?
-
Is the NEXTFLEX Cas9-gRNA Mito Depletion Enzyme (Human) suitable for degraded or low-input samples?
-
How much mitochondrial reduction can I expect?
-
Does mitochondrial depletion affect nuclear reads or introduce bias?
-
Can this module be used in DASH-style workflows or alongside other Cas9-based depletion modules?
-
Can I use the NEXTFLEX Cas9-gRNA Mito Depletion Enzyme (Human) in single-cell or single-nucleus workflows?
-
Should I use this product if I want to study mitochondrial DNA variants, copy number, or heteroplasmy?
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
Flyer describing the benefits of the NEXTFLEX Cas9 gRNA Depletion Enzymes.


Loading...
How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.