
NEXTFLEX Rapid Directional RNA-Seq Kit 2.0



| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Automation Compatible | Yes |
| Product Group | RNA-seq |



Product information
Overview
- High coverage uniformity with very low duplicate reads
- Input flexibility – 5 ng – 5 µg total RNA or 5 ng – 1 µg rRNA-depleted RNA
- Reverse-transcriptase and cleanup/size-selection beads are supplied in-kit
- Tested with NEXTFLEX Poly(A) Beads 2.0 and NEXTFLEX RiboNaut rRNA Depletion for directional detection of coding and non-coding transcripts (including lncRNA)
- Works with NEXTFLEX RNA-Seq 2.0 UDI barcodes for 2 – 384-plex runs or 96-plex UDI-UMI adapters to curb PCR duplicates
- Automation-ready
- Compatible with Illumina® and Element Biosciences™ AVITI™ sequencers
Additional product information
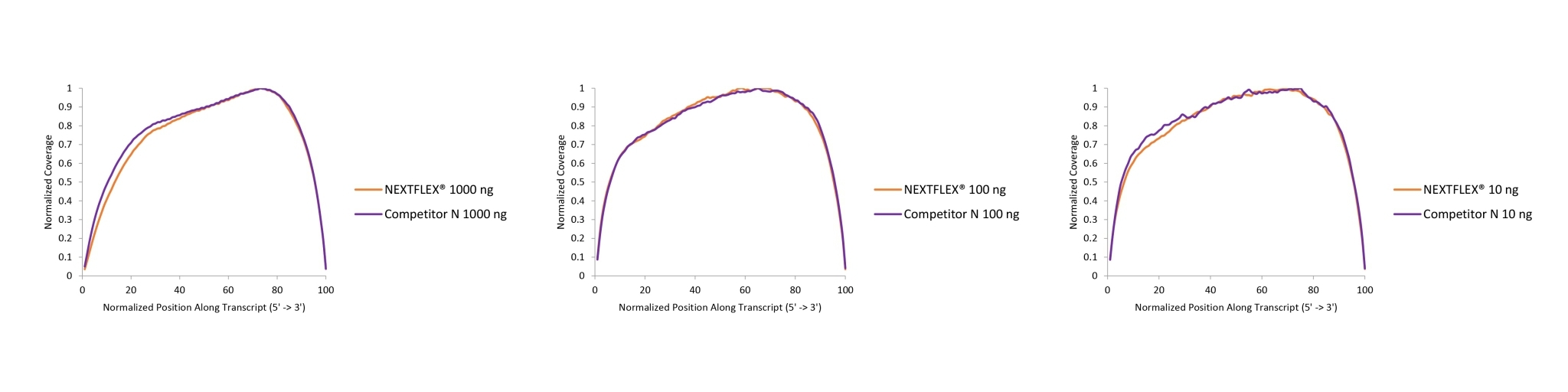
Consistently uniform coverage with ultra-low duplicates
The consistent read depth across exons delivered by the NEXTFLEX Rapid Directional RNA-seq Kit 2.0 improves the reliability of differential-expression calls and isoform quantification and enables improved detection of long or GC-rich transcripts without the need for bioinformatic smoothing or extra sequencing depth to compensate for bias.

Figure 1. The NEXTFLEX Rapid Directional RNA-Seq kit 2.0 demonstrates even coverage along transcripts compared to the Competitor N kit.
Lower duplication reflects higher library complexity, allowing deeper effective coverage per lane, reducing the risk of PCR artifacts, and cutting cost because fewer total reads are needed to achieve the same unique depth, critical for large, multiplexed studies.
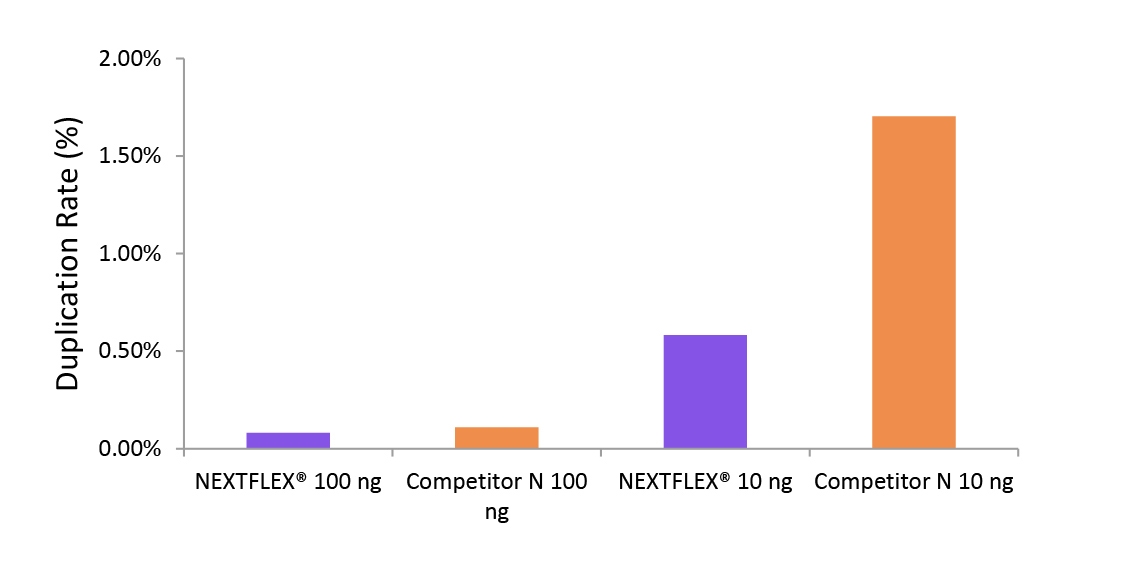
Figure 2. The NEXTFLEX Rapid Directional RNA-Seq kit 2.0 demonstrate low duplication rate compared to the Competitor N kit.
For more information & data, check out our application note here.
Flexible input range and ready-to-use reagents
From low-nanogram inputs harvested from precious biopsy samples to microgram quantities from cultured cells, the NEXTFLEX Rapid Directional RNA-seq Kit 2.0 streamlines the workflow, so you can progress from RNA to libraries with minimal additional setup. Reverse-transcription and size-selection chemistries are optimized to maintain uniform coverage and high library complexity across this entire input span, allowing a single protocol to serve both low-input discovery projects and high-throughput expression studies.
Seamless integration with NEXTFLEX accessories
The NEXTFLEX Rapid Directional RNA-seq Kit 2.0 kit plugs straight into Revvity’s wider NEXTFLEX RNA-seq accessory portfolio, letting you tailor each run to your sample type and throughput. Upstream choices include Poly(A) Beads 2.0 for fast mRNA enrichment and RiboNaut rRNA Depletion for total-RNA or degraded-sample workflows. Downstream, you can expand from small pilot sets to 384-plex studies with RNA-Seq 2.0 UDI or UDI-UMI adapter plates, adding molecular barcodes when duplicate suppression is critical. Every batch is color-balanced and QC-verified for index purity, protecting you from barcode bleed-through in large pools.
Explore the full accessory line to build a workflow that scales from low-input discovery to high-throughput clinical research without swapping vendors or protocols. For plant transcriptomics, the NEXTFLEX Rapid Directional RNA seq Kit 2.0 has been successfully paired with the Pan Plant riboPOOL to remove plant rRNA.
Automation-ready with 30 minutes of hands-on time
Pre-built scripts for the Sciclone G3 NGSx and Zephyr G3 NGS workstations cut hands-on time to <30 min for a full 96-well plate while preserving the coverage and duplicate metrics shown in Figures 1 and 2. That makes the workflow ideal for core labs balancing speed, reproducibility, and walk-away convenience.
Power your functional-genomics workflow with Revvity gene-modulation reagents
From hypothesis-free CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screens to precise CRISPRa/i activation or interference assays, Pin-point™ base editing, and well-established Dharmacon™ RNAi libraries, Revvity delivers every modality you need to probe gene function. Entire collections come in pooled or arrayed formats, to either increase or silence the expression levels of your gene of interest as part of your functional studies.
Synthetic sgRNA pools eliminate cloning and viral-packaging steps, while Pin-point™ base-editing reagents introduce precise, programmable single-nucleotide substitutions, an ideal approach for modelling disease alleles or drug-resistance mutations. Explore the complete CRISPR, RNAi, and base-editing portfolio.
Faster RNA-seq pooling for directional workflows
Use NEXTFLEX NGS Library Normalization Beads after PCR to standardize molarity across rRNA-depleted and poly(A)-selected libraries. You can pool immediately without separate quantitation, which helps keep large, multiplexed studies on schedule while maintaining even read counts across samples.
Specifications
| Automation Compatible |
Yes
|
|---|---|
| Format |
Automation Friendly Volumes
|
| Product Group |
RNA-seq
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Dual Temperature
|
| Unit Size |
48 rxns
|
Citations
De novo transcriptomes & non-model-organism genomics
- Bond, D. M., Ortega-Recalde, O., Laird, M. K., et al. (2023). The admired brushtail possum genome reveals invasion history in New Zealand and novel imprinted genes. Nature Communications, 14, 6364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41784-8
- Gaonkar, C. C., & Campbell, L. (2023). De novo transcriptome assembly and gene annotation for the toxic dinoflagellate Dinophysis. Scientific Data, 10, 345. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-023-02250-8
- Smith, C. H., Mejia-Trujillo, R., Breton, S., Pinto, B. J., Kirkpatrick, M., & Havird, J. C. (2023). Mitonuclear sex determination? Empirical evidence from bivalves. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 40(11), msad240. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msad240
- Chen, C., Tjeng, R., & Mueller, J. (2024). De novo transcriptome assembly and gene annotation for the toxic dinoflagellate Karenia. Scientific Data, 11, 34. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-023-02250-8
- Feke, A., Vaillancourt, B., Acheson, K., et l (2025). High resolution diel transcriptomes of autotetraploid potato reveal expression and sequence conservation among rhythmic genes. BMC Genomics. 26(1):925. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-025-11945-8.
Disease & functional-genomics models
- Laudadio, I., Carissimi, C., Scafa, N., et al. (2024). Characterization of patient-derived intestinal organoids for modeling fibrosis in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflammation Research, 73, 1359–1370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-024-01901-9
- Manukjan, N., Chau, S., Caiment, F., et al. (2024). Wnt7a decreases brain endothelial barrier function via β-catenin activation. Molecular Neurobiology, 61, 4854–4867. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03872-0
- Tóvári, J., Vári-Mező, D., Surguta, S. E., Ladányi, A., Kígyós, A., & Cserpes, M. (2023). Evolving acquired vemurafenib resistance in a BRAF V600E mutant melanoma PDX model to reveal new potential targets. Cells, 12, 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12141919
- McCarlie, S., Boucher-van Jaarsveld, C., & Bragg, R. (2024). Differential expression analysis reveals possible new quaternary ammonium compound resistance gene in highly resistant Serratia sp. HRI. Microorganisms, 12(9), 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091891 RNA chemistry, translation & isoform diversity
- Mulroney, T. E., Pöyry, T., Yam-Puc, J. C., et al. (2024). N1-methylpseudouridylation of mRNA causes +1 ribosomal frameshifting. Nature, 625, 189–194. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06800-3
- Higdon, A. L., Chemmama, I. E., Yao, T., … & Inada, T. (2024). Truncated protein isoforms generate diversity of protein localization and function in yeast. Cell Systems, 15(4), 388–408.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2024.03.005
- Grossi, E., Nguyen, C.B., Carcamo, S., et al (2025). The SWI/SNF PBAF complex facilitates REST occupancy at repressive chromatin. Mol Cell. 85(9):1714-1729.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2025.03.026.
- Bajtai E., Kiss, C., Bakos, É., et al. (2025). Therapy-induced senescence is a transient drug resistance mechanism in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 24(1):128. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-025-02310-0.
Stable non-coding RNA / aging
- Kirio, K., Patop, I. L., Martin Anduaga, A., Harris, J. M., Pamudurti, N., Su, T. N., Martel, C., Kadener, S. (2025). Circular RNAs exhibit exceptional stability in the aging brain and serve as reliable age and experience indicators. Cell Reports, 44(1), 115485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115485
FAQs
-
What types of RNAs are going to be detected with the NEXTFLEX Rapid Directional RNA-seq Kit 2.0 library?
-
What is the starting material I need to use to prepare libraries with this kit?
-
Are the libraries produced by NEXTFLEX Rapid Directional RNA-seq 2.0 stranded?
-
Is this kit compatible with RNA enrichment?
-
Do you offer solutions for depletion of rRNA, globin and others?
-
Is this kit compatible with FFPE-derived/low-quality RNA?
-
Can this kit be used to study long non-coding RNA?
-
Can this kit be used to study circular RNA?
-
What kind of barcodes can be used with the NEXTFLEX Rapid Directional RNA-seq 2.0?
-
Does this kit support long-read sequencing?
-
What are the recommended settings for sequencing?
-
What is the number of reads required for RNA sequencing?
-
What do I need to do to run the NEXTFLEX Rapid Directional RNA 2.0 libraries on the AVITI™ sequencer from Element® Biosciences?
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
This flyer illustrates the breadth of the NEXTFLEX RNA-seq Portfolio


Loading...
How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.