Automated counting of cytolytic plaques for plaque formation assay in large format microplates
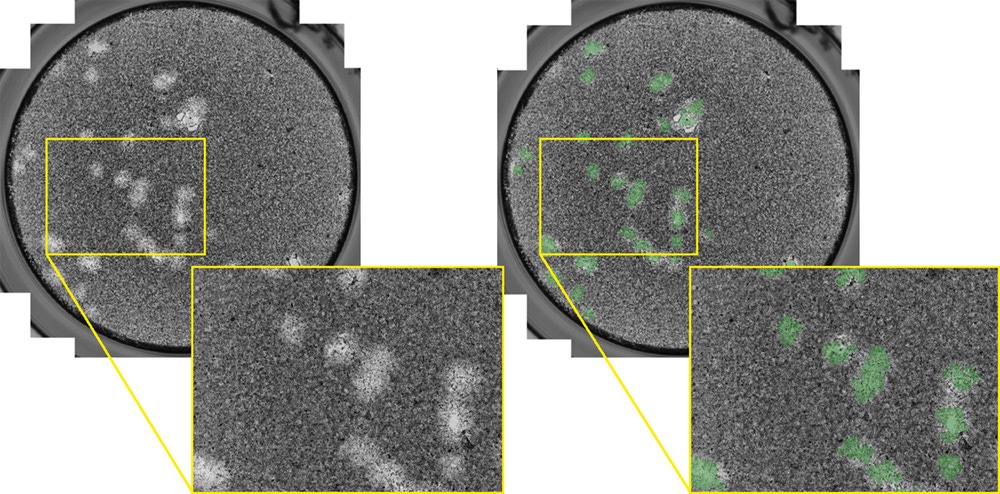
Cytolytic plaques are formed after a confluent monolayer of host cells are infected with the target viral particles, causing the cells to lyse. After a specific time duration, the viral infection can generate large openings, where the contrast can be enhanced by staining the host cells with crystal violet. Typically, these openings are manually counted with the naked eye. Utilizing the Celigo image cytometer, the cytolytic plaques can be automatically imaged and counted in less than 5 min/plate using brightfield. Below are examples of the whole well and zoomed-in brightfield images of cytotolytic plaques, as well as the counted image showing accurate identification of the plaques.

Whole well and zoomed-in brightfield images of cytolytic plaques formed in a 6-well plate. The plaques were directly counted in the Celigo software, where the counted image showed identification of the plaques.
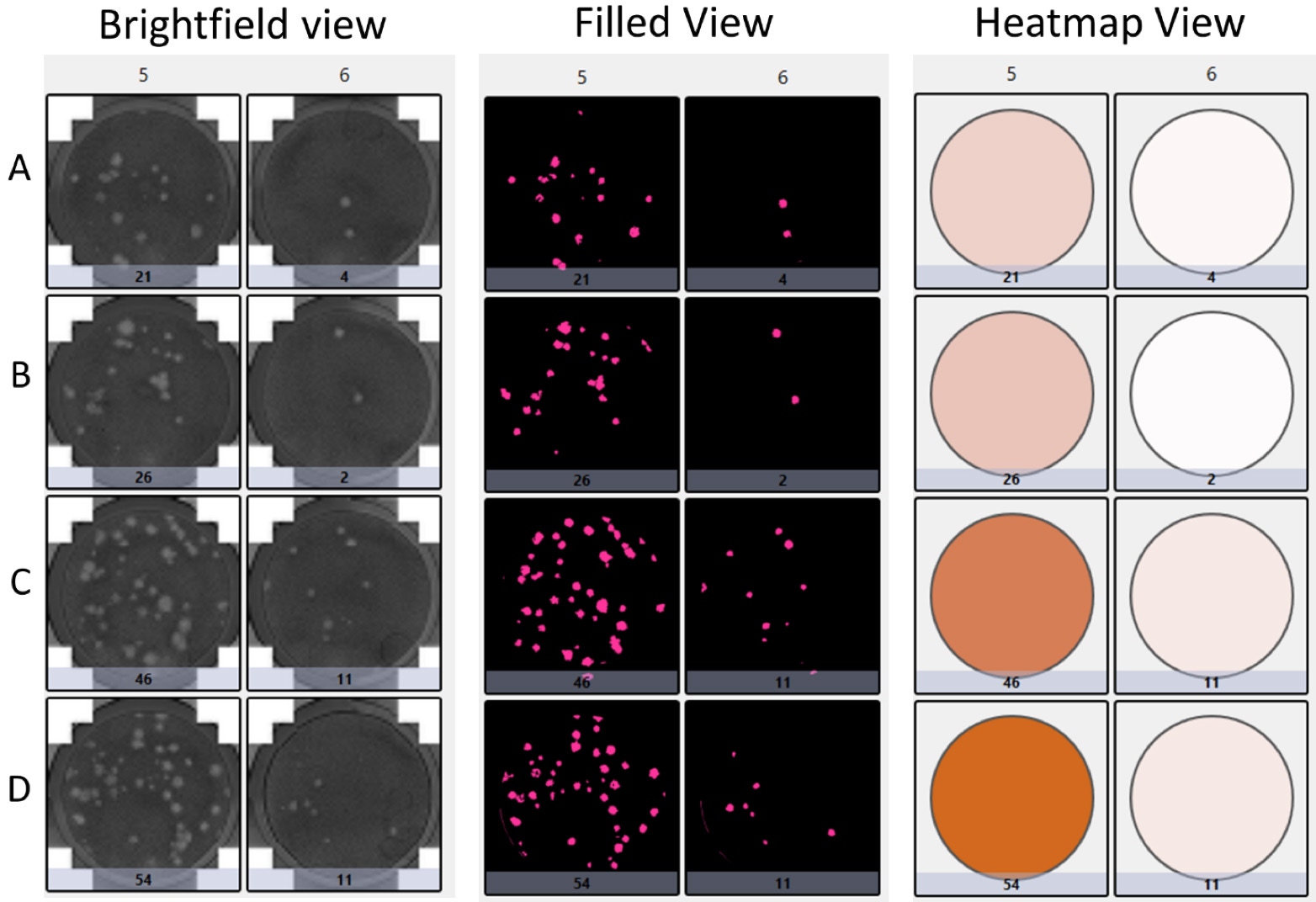
Plate view of the cytolytic plaques with brightfield, pseudo-filled color, and heat-map view in 24-well plates
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.




























