Typically, scientists perform the plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT) and the focus reduction neutralization test (FRNT) to determine the effectiveness of antibody treatments.
What is the plaque reduction neutralization test?
The plaque reduction neutralization test is considered the “gold standard” for detecting and measuring neutralizing antibodies for many disease-causing viruses.
- Antibody effects on viral infectivity are measured by plating virus-antibody mixture on virus-susceptible cells
- The cells are overlaid with a semi-solid medium that restricts spread of progeny virus
- The virally induced productive infection leads to a localized zone of clearing (a plaque), that can be detected in a variety of ways
- The number of counted plaques are used to determine the reduction in viral infectivity compared to the antibody-free mixture

What is the focus reduction neutralization test (FRNT)?
FRNT was developed because some viruses do not kill cells and therefore do not form the cytolytic (open) plaques.
- Foci are groups of infected cells that can be counted
- Foci are identified by examining stained cells with antiviral antibodies and are detected with a colorimetric substrate (horseradish peroxidase) or fluorescent labels
- Foci are manually counted to determine the neutralization effects
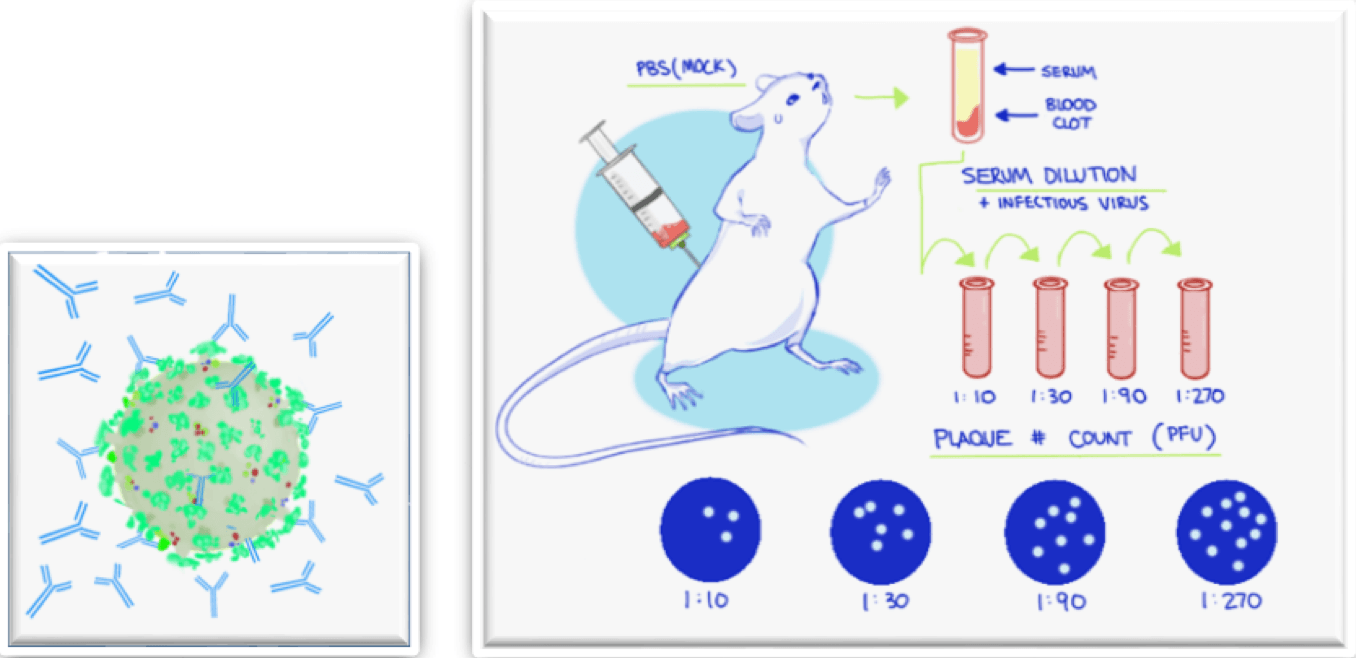
Neutralization using antibodies or directly with serum to prevent viral infection
- First, identify the multiplicity of infection (MOI) of the virus to be used for the neutralization assay
- Next, the host cells are infected with the virus at a specific MOI and treated with different dilutions of the neutralizing antibodies or sera
- Each antibody or sera dilution is quantitatively analyzed by looking at the reduction of plaques, foci, or individual infected cells
- Finally, the neutralization capabilities of the antibodies or sera are determined from the IC50 calculation
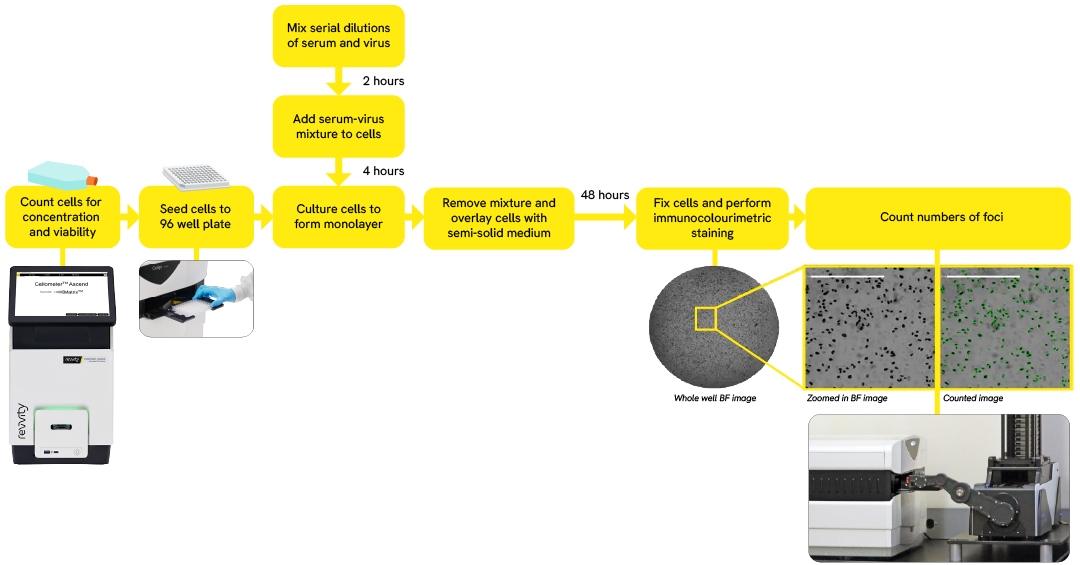
How is the virus neutralization measured?
Traditionally in the virus neutralization assay, the plaques, foci, or individual infected cells are counted manually using a standard microscope or by naked eye in the lightbox, as well as plate reader and conventional flow cytometer
| Detection method | Description | Existing issues |
|---|---|---|
| Naked eye (lightbox) | Manual counting of large cytolytic plaques (PRNT) stained with crystal violet in 6- or 12-well plates. | Low-throughput, labor-intensive, time-consuming, operator-variation, requires large volume (6, 12, 24-well plates), no digital records |
| Standard microscopy | Manual counting of small foci or individual infected cells labeled with horseradish peroxidase in 96-well plates. | Low-throughput, labor-intensive, time-consuming, operator-variation, no digital records |
| Digital automated microscopy | Automatic acquisition of fluorescent images of small foci or individual infected cells labeled with fluorescent probes (i.e., immunostaining or fluorescent proteins). Next, use of external software (i.e., ImageJ) to automatically analyze and count the small foci or individual infected cells. | Time-consuming, not streamlined, requires multiple steps |
| Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) using a plate reader | Measurement of the binding signals in fluorescence of the potential neutralizing antibodies to the neutralization epitopes | Indirect method, requires multiple assay steps to complete |
| Flow cytometry | Automatic counting and analysis of the population of individual infected cells labeled with fluorescent probes (i.e., immunostaining or fluorescent proteins) | Time-consuming, requires trypsinization of host cells from plates, cannot detect large plaques or foci, must use fluorescent labeling |
Novel modern cell-based microneutralization assays using the Celigo Image Cytometer
The Celigo™ image cytometer
 Celigo Image Cytometer
is a high-throughput and high-speed plate imager that can rapidly image the entire microplate in bright field and fluorescence, to produce counts, morphology, and intensity measurements.
Celigo Image Cytometer
is a high-throughput and high-speed plate imager that can rapidly image the entire microplate in bright field and fluorescence, to produce counts, morphology, and intensity measurements.
- Simultaneous image acquisition and analysis in less than 10 min/plate
- Automatically count plaques, foci, or individually infected cells in whole well 96- and 384-well plates
- Directly count total and infected number of cells in whole well to rapidly generate infectivity rates
- Measure infectivity rates by counting cells directly in the well without trypsinization
- Time-course monitoring of viral infection through the detection of cytolytic plaque, fluorescent protein-expressing foci or infected cells
- Addition of plate stacker automation allows a throughput of 50 plates analyzed per day
You may also be interested in these products





For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.




























